Nowadays, credit card fraud represents a major threat to businesses and consumers. Credit card usage has become a fundamental part to people’s daily lives, which increases both the risk and concern around fraud. The number of credit card users worldwide has increased, which has resulted in a higher incidence of fraud cases. While companies that work on credit card protection and financial organizations are doing their best to prevent fraud and its consequences, the number of unfortunate incidents is forcing businesses to implement state-of-the-art solutions to protect their customers.
Traditional systems are failing to keep up as advancing cybercriminal approaches; credit card fraud detection using machine learning, on the other hand, is quickly becoming the new standard for safety and protection. In this article, we will focus on the details of this movement, from examining the causes and consequences of credit card abuse to highlighting the profound effect of machine learning in reimagining detection methods.
How Does Credit Card Fraud Happen?
Credit card fraud has a multitude of forms, showcasing a wide variety of deceptive tactics. Below, we highlight eight of the most prevalent types.

- Card Present Fraud: This type of fraud occurs when a fraudster physically presents a counterfeit or stolen credit card for payment at a merchant location. It may involve using altered or cloned cards to make purchases.
- Card Not Present (CNP) Fraud: CNP fraud happens when the cardholder’s information (such as card number, expiration date, and security code) is stolen and used to make fraudulent transactions online, over the phone, or via mail order. Since the card is not physically present, it’s often easier for fraudsters to carry out these unauthorized transactions.
- Account Takeover: In an account takeover, fraudsters gain unauthorized access to a legitimate cardholder’s account information, often through phishing scams, malware, or data breaches. Once they have control of the account, they make fraudulent purchases, change account details, or transfer funds without the cardholder’s knowledge.
- Lost or Stolen Card Fraud: This fraud occurs when credit cards are physically lost or stolen, and unlawful transactions are made using the cards before the cardholders report them missing. Fraudsters use the stolen card to make purchases or withdraw cash until the card is canceled or blocked.
- Identity Theft: This type of scam involves fraudsters using stolen credit card details, including social security numbers, addresses, and dates of birth, to open new credit card accounts or take over existing ones. They apply for credit cards in the victim’s name and use them for unauthorized transactions, leaving the victim liable for the charges.
- Skimming: In this case, installed devices, or card skimmers, are used on legitimate card readers, such as ATMs, gas pumps, or point-of-sale terminals, to capture card data when the card is swiped or inserted. The stolen credit card details are then used to create counterfeit cards or make unlawful transactions.
- Phishing: These scams involve fraudsters sending deceptive emails, text messages, or phone calls posing as legitimate institutions to trick individuals into revealing their credit card information, login credentials, or other sensitive data. Once obtained, cardholders’ details are used for different types of fraud, including CNP fraud and identity theft.
- Application Fraud: Fraudsters submit fraudulent credit card applications using stolen or fabricated personal information. They use fake identities or stolen documents to obtain credit cards, which are used for unauthorized transactions or sold on the black market.
The Impact of Credit Card Fraud In Facts and Numbers
Unfortunately, fraud-related incidents can cause massive damage and long-term impact, not only for people but also for entire organizations, from small ones to large enterprises. The victims face a wide spectrum of harmful consequences, including reputational harm, financial losses, legal expenses, and devastating business interruptions. Let’s take a closer look at the most common scenarios.
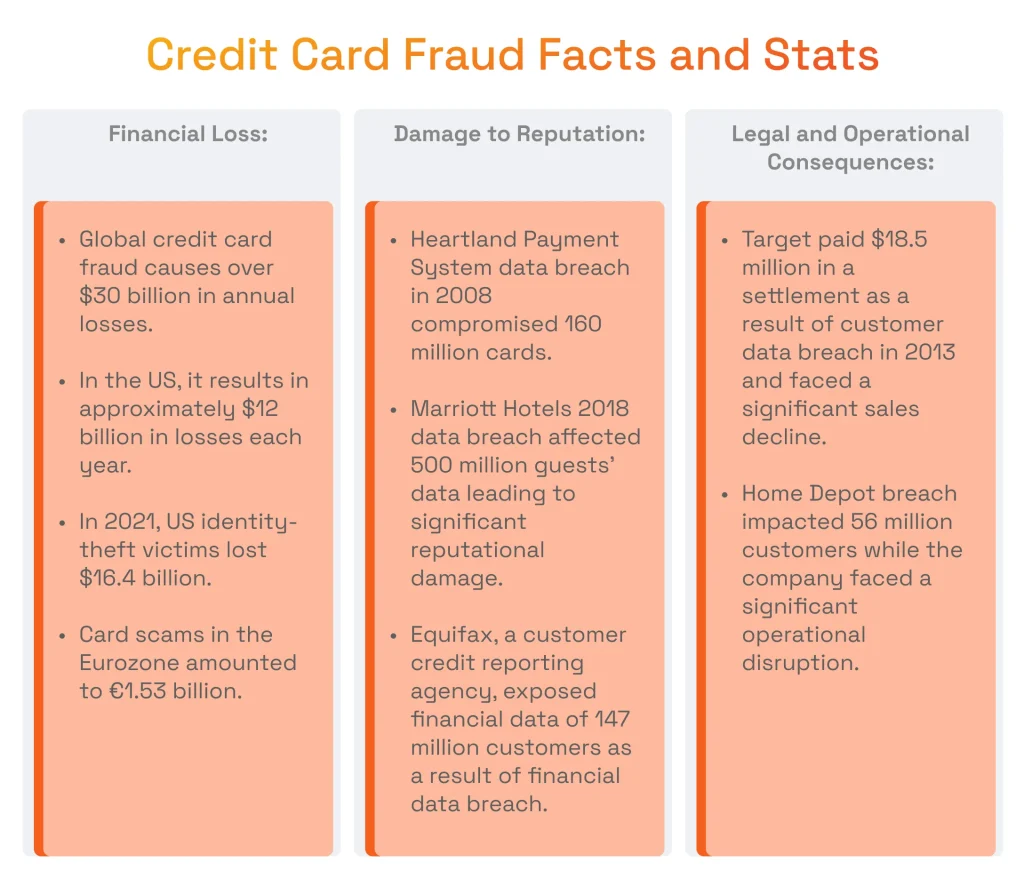
Financial Loss
When fraud occurs, businesses can suffer direct financial losses from fraudulent credit card transactions. They may face additional costs such as chargeback fees, fines, and increased transaction processing expenses associated with implementing fraud prevention measures.
- Credit card fraud results in billions of dollars in losses annually. Globally, merchants and card acquirers have suffered losses exceeding 30 billion U.S. dollars, with approximately 12 billion U.S. dollars stemming from the United States alone.
- In 2021, approximately 59% of identity-theft victims experienced financial losses of $1 or more, amounting to a total of $16.4 billion in the US, as stated by the Bureau of Justice Statistics.
- According to the European Central Bank, card scams constituted 0.028% of the total value of card payments made using cards issued in the Single Euro Payments Area, amounting to €1.53 billion from a total value of €5.40 trillion.
Damage to Reputation
Incidents of financial card fraud damage a business’s reputation and damage consumer trust. Customers start to perceive the business as insecure or unreliable if their transaction data is compromised, causing a decline in sales, negative reviews, and loss of customer loyalty.
- The 2008 data breach at Heartland Payment Systems, caused by malware on its payment processing network, compromised 160 million credit and debit cards. This led to major financial and a negative impact on the company’s reputation. Heartland encountered many lawsuits from financial institutions and cardholders seeking damages for the unauthorized charges and losses incurred as a result of the breach. Even though the data breach occurred in 2008, such reputational consequences remain relevant in 2024.
- The Marriott data breach in 2018 severely damaged the company’s reputation. Hackers gained unauthorized access to the guest reservation database, compromising the personal information, including credit cards, of approximately 500 million guests. Marriott underwent major backlash and negative publicity, with many customers voicing displeasure and concerns about the safety of their personal information.
Legal and Regulatory Consequences
Businesses that fail to implement adequate precautionary steps to shield against fraudulent charges face legal consequences. Depending on the jurisdiction and industry, they are subject to fines, lawsuits, or sanctions for non-compliance with data security standards and consumer protection laws.
- A major retailer Target dealt with serious legal consequences as a result of the credit card scam incident. The company agreed to pay $18.5 million to 47 states and the District of Columbia in a settlement with state attorneys general. This settlement concluded a years-long investigation into the breach, which compromised the data of millions of customers in 2013. Target also incurred substantial legal fees and costs totaling $202 million.
- Another example is the Equifax data breach in 2017, where hackers gained access to financial data of approximately 147 million consumers. Equifax encountered severe legal and regulatory scrutiny, including multiple lawsuits and investigations by state and federal authorities. The company ultimately reached settlements with regulators and agreed to pay significant fines to resolve the legal and regulatory actions against it.
Operational Disruption
Dealing with the aftermath of credit card scam, including investigating incidents, reimbursing affected customers, and implementing fraud mitigation strategies, may interrupt regular business operations and divert resources away from core activities.
- During the Home Depot data breach in 2014, hackers gained access to Home Depot’s payment systems, compromising the credit and debit card information of approximately 56 million customers. The company suffered a decline in sales as well as client trust following the breach, as many customers were concerned about the security of their payment information.
- Operational interruptions and delays were also consequential for Target, mentioned above. The retail chain had to dedicate resources to investigate the breach, cyber defense strategies, and provide help for affected customers. Additionally, the breach resulted in a decrease in sales.
The Benefits of Credit Card Fraud Detection with Machine Learning Over Traditional Methods
Traditional credit card fraud monitoring is built on predefined rules and patterns but struggles to keep pace with advancing tactics. In contrast, fraud detection with machine learning harnesses the power of advanced algorithms for identifying patterns of suspicious activity efficiently. An ML model for credit card fraud detection is trained on historical transaction data to identify patterns that distinguish fraudulent from legitimate activity, allowing proactive risk management.
The following comparison explores the principles behind both methods in combating fraudulent transactions.
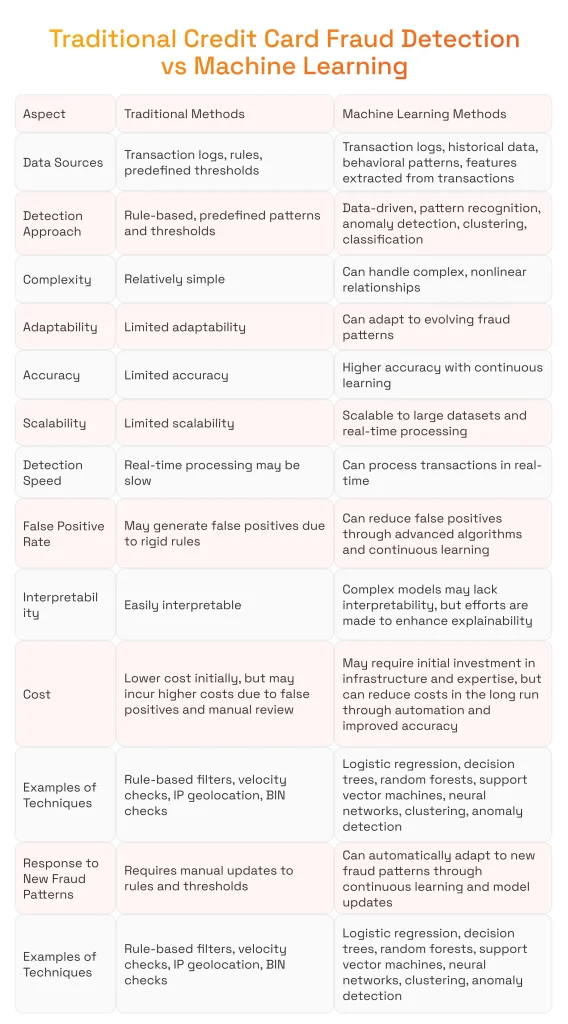
The dataset used for training typically contains a large number of transactions with features describing each transaction. The model is typically trained on a dataset of historical transactions and evaluated on a separate holdout dataset of previously unobserved transactions to measure performance.
In contrast to traditional fraud detection methods, ML for credit card fraud detection revolutionizes card scam detection by providing a range of advantages. Thanks to the following aspects, credit card fraud detection using ML provides unsurpassed defense against fraud schemes. These models help figure out which transactions are fraudulent by identifying patterns that indicate suspicious activity.
Improved Accuracy
The impact of big data on business makes companies use ML algorithms to generate insights. These algorithms discern sophisticated patterns and anomalies in the data, guaranteeing unmatched accuracy in detecting fraud schemes. By examining extensive amounts of transaction data and user behavior, ML models can distinguish between legitimate and fraudulent payments with high precision, minimizing false positives and negatives.
Adaptability to New Threats
Continuously learning from fresh data, ML models quickly detect and counter emerging fraud schemes. Whether it’s discerning sophisticated phishing efforts, combating account takeover fraud, or exposing new identity theft techniques, ML systems stay steps ahead through automatically updating their fraud detection approaches. This is one of the most important aspects of how ML models help with fraud detection in the timely detection of new threats.
Detection of Complex Fraud Schemes
Traditional rule-based fraud detection systems frequently face challenges to detect complex fraud schemes that involve multiple variables and fine-grained patterns. ML, on the other hand, excels at revealing concealed correlations and non-linear relationships within data, rendering it especially effective in identifying complex fraud schemes. By employing cutting-edge algorithms such as neural networks, decision trees, and ensemble methods, ML models can detect even the most sophisticated fraud attempts that may evade conventional detection techniques.
Complex credit fraud scheme detection is an essential part of banking security, critical to preventing financial losses, conforming to regulatory compliance, and building customer trust. By applying innovative detection systems, banks can swiftly find suspicious activities, defending both their reputation and customers’ assets. Automated processes not only increase operational performance but also offer meaningful understanding of developing threats, allowing proactive adaptation of security measures. Effective fraud detection does more than protect the bank’s bottom line and also guarantees a strong and trusted financial network for all stakeholders.
Willing to know how ML can transform the banking industry?
Find out in our featured article!
Reduced Manual Intervention
ML automates many aspects of the fraud detection process, minimizing the requirement for manual intervention and manual supervision. With automation and predictive analytics, ML systems are able to analyze and flag potentially scam real-time transactions, allowing fraud analysts to focus their attention on investigating high-risk cases and developing proactive approaches to reduce fraud.
When Implementing Credit Card Fraud Detection with ML Makes Sense?
When exploring the terrain of credit card fraud detection, certain scenarios emerge where the embedding of ML is especially advantageous. Analyzing transaction trends—behavioral features and trends in transaction data—can help determine when ML-based fraud detection is most beneficial. Additionally, behavioral biometrics, which analyzes user-specific patterns like typing speed and swipe gestures, can improve identity verification in fraud identification solutions.
High Volume of Transactions
In settings defined by a high volume of transactions, machine learning in fraud detection can efficiently study massive amounts of data as it happens. With its real-time data analysis functions, ML swiftly dissects vast data streams, pinpointing fraudulent patterns among the legitimate transactions’ torrential flow.
Machine learning for retail proves to be advantageous as it excels at quickly processing and analyzing wide-ranging datasets, which include transaction specifics, client engagements, and other pertinent data.
New Market Entry
When entering new markets or expanding globally, businesses may encounter unfamiliar fraud patterns and risks. ML performs exceptionally well in responding to new environments, employing historical transactional data and continuous learning to detect fraudulent behavior unique to specific regions or markets. Such flexibility makes ML-based fraud detection particularly suitable for organizations venturing into unexplored areas.
High Risk and Cross Border Transactions
Transactions involving high-risk activities or cross-border transactions are inherently more susceptible to fraud. ML algorithms, with their ability to analyze different data inputs and detect fine-grained patterns, provide advanced capacities for identifying fraudulent transactions in these scenarios. By closely evaluating transaction intricacies, user behavior nuances, and geographical details, ML algorithms meticulously flag suspicious transactions.
Upcoming Integrations with Third-Parties
Expanding business operations through integrations with payment gateways or third-party platforms deliver more opportunities but also escalates fraud risks. ML-powered fraud detection can vigilantly track transactions within partner networks, swiftly identifying and thwarting unauthorized operations originating from integrated systems.
Discover how to seamlessly integrate a payment gateway into your website, ensuring its security!
Credit Card Fraud Detection with Machine Learning: Development and Implementation
Based on the table above we can say that machine learning for finance is an advanced way for card fraud monitoring, preferred by businesses endeavoring to elevate software security. Businesses often develop ML models specifically for credit card fraud detection, training these models on historical transaction data to identify and prevent fraud schemes.
According to the Statista report, nearly 40% of companies used automation systems, including ML-based solutions, for fraud detection in 2023. But what are the steps involved in preventing fraud using ML? The procedure starts with the following seven stages.
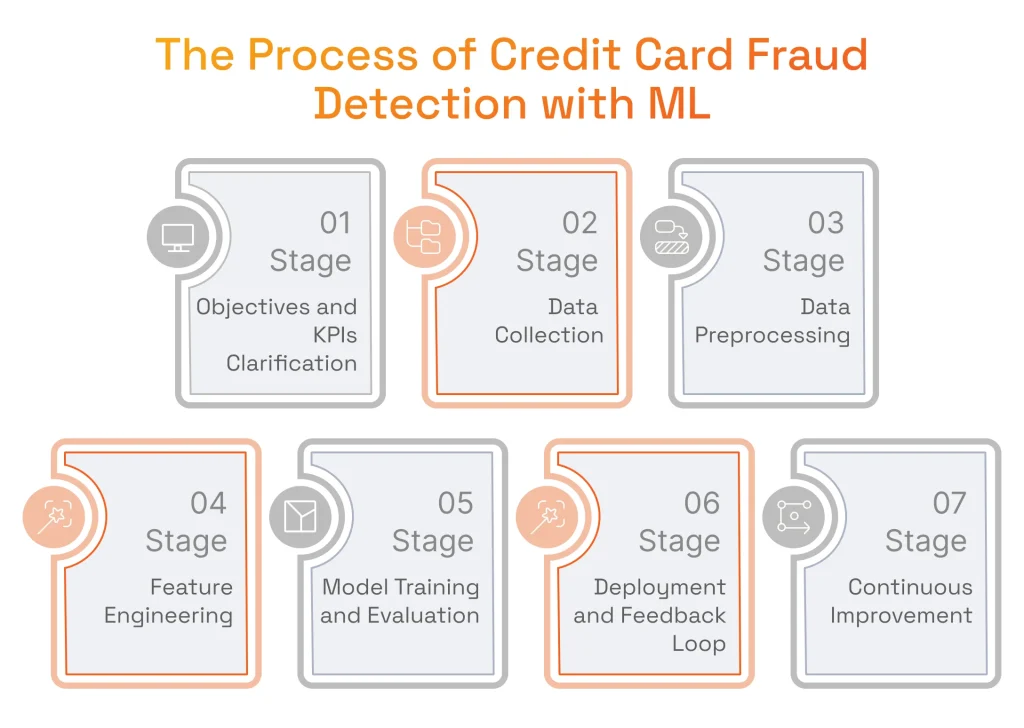
Stage 1: Objectives and KPIs Clarification
It will be a good idea to start through aligning your ML initiative consistent with organizational targets and objectives. Every business that wants to implement fraud detection strives to reduce fraud-related losses while making certain that security measures will not negatively affect customer experience.
So, before moving to the rollout steps, it is important to set specific KPIs for your solution, including accuracy, precision, recall, and false-positive rates. Additionally, make an effort to strike a perfect balance between detecting fraud and not slowing down the speed of transactions for end users. Work with your team on how your future solution will achieve that on a strategic level.
Stage 2: Data Collection
In the context of preventing credit card scams, it comprises collecting data from different sources such as transaction logs, customer information databases, device details, external data sources, and historical fraud data. Gathering diverse and thorough training data from multiple sources is vital to improve the model’s ability to detect various fraud scenarios and increase overall system strength. Data preparation usually entails loading the dataset into a DataFrame and reviewing its structure to understand the features available for modeling. Additionally, data streaming technologies like Apache Kafka and Apache Flink are standard tools for live data ingestion and processing, supporting immediate detection of fraud schemes.
However, the raw data obtained from these sources often contains inconsistencies, missing values, outliers, and other issues that need to be addressed before it can be effectively used to spot frauds.
Stage 3: Data Preprocessing
To clean, transform, and prepare the raw data for analysis, ML engineers apply data preprocessing techniques. This involves several steps:
- Examination: Before preprocessing, it is important to check the shape of the dataset to understand its dimensions (number of rows and columns). Using print statements in code to output the shape and other characteristics of the data during preprocessing helps in debugging and verifying data integrity.
- Data Cleaning: Involves handling missing values, correcting inconsistencies, and removing duplicates. For example, missing values in transaction amounts or timestamps might be imputed using statistical methods or filled with appropriate defaults.
- Outlier Detection and Handling: Outliers can significantly affect the performance of ML models. Techniques such as Z-score, interquartile range (IQR), or clustering-based approaches can be used to detect and handle outliers.
- Feature Scaling: Features in the dataset may have different scales, which can lead to biased models. Techniques such as normalization or standardization are applied to bring all features to a similar scale.
- Encoding Categorical Variables: Categorical variables such as merchant IDs or transaction types need to be encoded into numerical representations before being fed into ML algorithms. Techniques like one-hot encoding or label encoding are commonly used for this purpose.
- Feature Engineering: Feature engineering included creating unique identifiers for merchants and customers, as well as temporal features like ‘is_weekend’ and ‘is_night’ to capture transaction patterns.
- Data Transformation: Transformation techniques like logarithmic transformation or Box-Cox transformation may be applied to make the data more symmetrical and improve model performance.
Stage 4: Feature Engineering
Next comes feature engineering crucial for enhancing the predictive power of ML models in fraud monitoring. It involves creating new features or variables that capture relevant information about fraudulent activities. Feature engineering techniques extract, transform, and aggregate information from the preprocessed data to create new features. Features are often transformed for privacy or modeling purposes, such as converting identifiers or applying dimensionality reduction. For example, PCA transformation can be applied to numeric variables to protect customer privacy while retaining essential patterns for analysis in detecting fraudulent transactions. Some common feature engineering techniques in monitoring frauds with financial card include:
- Time-Based Features: Features derived from transaction timestamps such as time of day, day of week, or time since last transaction. Fraudulent activities may exhibit specific patterns at short periods of time.
- Transaction Amount Statistics: Aggregations and statistics derived from transaction amounts, such as mean, median, standard deviation, maximum, minimum, and percentiles. Here, anomaly detection with machine learning helps to spot fraudulent behavior.
- Merchant and Customer Behavior Features: Features capturing patterns in merchant-customer interactions, such as frequency of credit card transactions with specific merchants, average transaction amounts per merchant, or unusual changes in spending behavior.
- Device and Location Features: Features related to the device used for transactions (e.g., device ID, IP address) and transaction locations (e.g., geolocation, distance between transaction locations). Sudden changes in device or location may indicate suspicious activity.
- Aggregated Features: Features derived from aggregating historical transaction data, such as the number of previous payments within a certain timeframe, or the frequency of transactions from high-risk locations.
Stage 5: Model Training and Evaluation
After feature engineering, ML models are trained on the preprocessed and feature-engineered data to learn patterns and generate predictions. The dataset is typically split into training and test data, with the test data used to evaluate how well the model applies to unseen transactions. Different ML algorithms such as logistic regression, random forests, gradient boosting, or deep learning models like neural networks are trained on the datasets.
These models are subsequently used to predict whether a given transaction is fraudulent or legitimate based on transaction data. The trained models are evaluated using evaluation criteria such as, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC on a separate test dataset to analyze their effectiveness in detecting fraudulent transactions. A confusion matrix is often used to visualize the number of true positives, false positives, true negatives, and false negatives, giving perspective on model strengths and weaknesses. It is important to note that imbalanced datasets can lead to misleading model effectiveness metrics, as high accuracy can be achieved by simply predicting the majority class. Techniques like cross-validation and hyperparameter tuning are implemented to boost model effectiveness and avoid overfitting.
Stage 6: Deployment and Setting Up Feedback Loop
Once evaluated, the best-performing model is deployed into production where it continuously monitors incoming payments, flagging potentially suspicious transactions for further review or action.
At this stage, one of the most important aspects is to establish an effective feedback loop and improve the performance of the model over time. Encouraging user engagement and collecting feedback from users or analysts is fundamental, as their engagement supports pinpoint opportunities for enhancement and refines the fraud detection system. This process includes regular data collection on flagged transactions, and manually reviewing outcomes of fraud investigations. The data from the reviews must be fed into the model, so the credit card fraud detection system using ML will be able to learn from the mistakes and reduce false positives.
Stage 7: Continuous Improvement
Right after the deployment, the process of continuous improvements begins, as there is no limit to perfection. Fraud patterns evolve constantly, so ensure that your model is kept updated with new information and is future-proofed to face upcoming threats. It is also very important to monitor data and model effectiveness for concept drift, where the statistical properties of the target variable change over time, decreasing model effectiveness.
Credit Card Fraud Detection Challenges and Considerations
Developing fraud detection in credit card operations software is one of the important trends in the payments industry. This happens because using machine learning to detect credit card fraud offers encouraging chances to strengthen security and lessen financial losses. Nevertheless, it also presents a number of challenges that need to be addressed.

Imbalanced Data
Unlawful transactions are typically rare compared to legitimate ones, resulting in imbalanced datasets in which the number of positive (fraudulent) instances is much lower than negative (legitimate) instances. Imbalanced data lead towards biased models that concentrate on accuracy at the expense of detecting suspicious transactions.
In our projects, we mitigate the imbalance and improve model effectiveness with the help of techniques such as resampling (e.g., oversampling minority class, undersampling majority class), cost-sensitive learning, and ensemble methods.
Interpretability of Models
The explainability of fraud detection machine learning models is key to knowing how they make decisions and gaining knowledge about the elements influencing fraudulent behavior. However, complex and opaque models, such as deep learning neural networks, may have low interpretability, rendering it difficult to trust and explain their predictions.
To deal with this challenge, we employ interpretable models, such as decision trees and logistic regression, whenever possible to boost transparency and trust in the fraud detection system. Additionally, to help explain the predictions of complex models, we leverage in our projects techniques such as feature significance analysis, model-agnostic explainability techniques, and model documentation.
Privacy and Ethical Concerns
Fraud detection systems often process sensitive personal and financial data, raising concerns about privacy violations, data breaches, and ethical considerations. One of the factors that can bring even more risks to privacy is human intervention since it creates the risk of human error or bias.
In practice, we implement robust data protection measures, such as encryption, access controls, and anonymized credit card transactions techniques to safeguard customer privacy and comply with data protection regulations. Additionally, automation helps us to ensure consistent adherence to privacy protocols. It has proven to reduce errors and enhance efficiency and scalability in handling large volumes of transactions while maintaining data privacy and ethical standards.
For instance, the Aggregated Merchant Portal (AMP) that we created for Blackhawk Networks, one of our major customers, allows the businesses to automatically pass OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control), EIN/SSN (Employer Identification Number / Social Security Number) and other legal entity ID checks.
Real-Time Detection
Detecting fraudulent transactions in real-time is critical to prevent financial losses and minimize the impact on customers. However, traditional ML models may be computationally expensive and time-consuming to process transactions in real-time.
We achieve real-time detection capabilities by deploying lightweight and scalable models, leveraging streaming data processing technologies, and implementing efficient feature engineering and model inference pipelines. We set up robust monitoring and alerting systems to quickly identify and respond to suspicious activities.
Time and Cost to Implement an ML-Based Credit Card Fraud Detection System
Implementing such a system is a very challenging and sophisticated process that requires a proficient team of experts, exceptional project management, and phased integration. In this section, we will talk about the required resources, timeframes, and financial considerations for fraud detection software development services.
Technical Resources
While the needs of each unique credit card fraud detection project using machine learning may vary, it is safe to say that the following categories are essential for every ML-powered fraud detection initiative.
Data Resources
- Historical Transaction Data: Large sets of data on both fraudulent and non-fraudulent transactions are required to train ML models for effective anomaly detection.
- External Fraud Databases or Partnerships: Your system will receive another level of computational intelligence when combined with external fraud detection services and shared databases.
- Data Collection and Storage Tools: These tools include secure databases, capable of handling large volumes of data with effective storage and retrieval mechanisms.
Machine Learning Infrastructure
- Cloud Infrastructure: Modern cloud platforms like AWS, Azure and Google Cloud allow developers to set up scalable computing environments for the best possible model training and real-time fraud detection at scale.
- Data Pipelines for Real-Time Transaction Data Flow: Real-time data processing is a fundamental element of fraud detection, and can be achieved by setting up effective data pipelines to transfer data to ML models from all required sources.
Software and Tools
- Machine Learning Frameworks: These frameworks offer a wide range of functionalities for developing advanced ML algorithms. The most prominent examples of frameworks include TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn.
- Data Visualization Tools: With solutions like Tableau and Power BI, it becomes very convenient to monitor system performance, and present actionable insights for stakeholders.
- Fraud Detection Platforms or APIs: You can also leverage fraud-detection-as-a-service solutions to boost your capabilities. With platforms like Fraud.net, Sift, and Kount, you will be able to have real-time fraud scoring for transactions, as well as additional insights on your processes.
Compliance and Regulatory Resources
- Tools and Systems to Meet Regulatory Requirements (GDPR, PCI DSS): When dealing with sensitive financial data, it is important to ensure compliance with GDPR and PCI DSS. Encryption solutions like Symantec Encryption and Consent Management Platforms (GDPR) like OneTrust are among some of the most important tools to help you achieve that.
- Cybersecurity Tools to Protect Customer Data: As for cybersecurity tools, it is important to mention endpoint protection and antivirus software like CrowdStrike, and intrusion detection software like Snort, as well as tokenization tools by Protegrity. However, there are plenty of off-the-shelf solutions, suitable for different use cases.
Human Resources
The success of your machine learning and fraud detection initiative is based on your expert team. Here are some of the key roles, that you, or your service provider, need to fulfill with exceptional talent to build the best solution possible:
- Data Scientists: They play a major role in designing training and optimizing ML models.
- Data Engineers: Focus on developing and managing the infrastructure for data ingestion, processing, and storage.
- Fraud Analysts: They bring the necessary domain expertise to validate the results of ML models.
- Legal Advisors: These specialists make sure that your fraud detection system adheres to all security regulations, industry standards, and compliance frameworks.
- Cybersecurity Experts: Your cybersecurity team will secure the infrastructure, protect sensitive data, and monitor the system for vulnerabilities.
- A Project Manager: The one who will ensure the smooth implementation of the project, coordinating teams, making deadlines, and curating the entire process.
Financial Resources
While every case is different, and it is important to offer one-size-fits-all budget estimations, these categories are valid for any ML-based credit card fraud detection solution.
- Budget for Infrastructure: Typically, cloud infrastructures are billed based on usage, so you need to allocate a chunk of your budget for computing services of AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, data storage and maintenance costs.
- Budget for Hiring Experts: Depending on the size, structure, and experience of each expert in your team, the overall staff budget may vary dramatically.
- Budget for Software and Tools: Many of the ML frameworks, fraud detection platforms, and data visualization tools are subscription-based services, so be prepared for a recurring cost here.
- Budget for Compliance: Finally, to meet regulatory requirements you will have to pay for legal consultation, compliance software, and regular audits.
Estimated Timelines for Phase 1 (3-6 Months)
The first phase of the implementation is probably the most important one since it should result in a fully functional proof-of-concept able to detect key fraud patterns. At this stage, the infrastructure should be determined, ensuring scalability and adaptability, and laying the groundwork for future improvements. Let’s break down the initial phase and explain the approximate timelines.
Month 1-2: Setup and Planning
The first two months typically are spent on setting up cloud infrastructure and adjusting data collection tools. In parallel, fraud experts and business analysts collaborate on defining key fraud patterns, as well as strong alignment with the business requirements and goals. These steps become a basis for the development of an effective fraud detection system in the future.
Month 3-4: Data Pipeline and Model Prototyping
Next, the project goes to the hands of data engineers, who build data pipelines and ensure the real-time flow of transaction data to the ML models. Simultaneously, data scientists are working on developing and testing the first model prototypes based on historical data on fraud patterns.
Month 5-6: Model Refinement and Integration
Data scientists put in a final effort to refine the models based on performance metrics and maximize the accuracy of fraud detection. Next, DevOps engineers are setting up the deployment pipelines smoothly, and the project goes into production. After the APIs are fully integrated into the existing system, the fraud detection functionality becomes available.
Consider Professional Machine Learning Development Services from SPD Technology
We, at SPD Technology, are here to help you overcome the challenges of developing and implementing an ML-based credit card fraud detection system with a high degree of accuracy and an emphasis on security.
Why Are Professional Services the Wise Option for ML-Based Credit Card Fraud Detection?
Choosing professional services over assembling your ML development team has several significant advantages. The most important one is access to the latest expertise in AI/ML. Since the technologies and approaches of criminals are always evolving, staying on top of cutting-edge trends is vital to secure the exceptional precision and efficiency of a custom fraud detection system.
It is preferable to have a strong team of experts proficient in the current technology stack that constantly deploys fraud detection solutions and knows how to implement them in the fastest time possible and with minimal-to-none disruptions to critical processes. Furthermore, in addition to detecting fraud, someone has to deliver a full risk assessment strategy, creating holistic approaches to potential risks.
With credit card fraud detection solutions there is also a requirement to align with every relevant legal framework, including GDPR, PCI DSS, and other regional regulations. Data security is of the utmost importance for credit card transactions, so professional services will help you adhere to industry-leading security protocols and encryption practices to protect sensitive financial data.
Why You Should Consider SPD Technology for This Goal
We believe that choosing our company is the best solution you can make in developing an ML-powered credit card fraud detection system, due to our long history of delivering best-in-breed custom software projects for global market leaders.
For over 18 years and beyond, we have been at the forefront of innovation in building highly tailored AI in Fintech solutions. We deeply understand the specific challenges of fraud detection, including handling large numbers of transactions, delivering real-time response capabilities, implementing the industry’s best practices, and following all necessary regulations. Our track record includes high-performing, high-scale platforms, such as our enterprise-level Omnicommerce Payment-Processing Platform, capable of processing millions of transactions per day while maintaining rigorous fraud prevention mechanisms.
When you partner with us, you get the support of your system through its entire lifecycle. We provide end-to-end support that includes initial consultation, design, development, deployment, and continuous monitoring and improvements. Our team delivers solutions that will easily perform payment gateways integration services, as well as connect your systems with CRM systems, legacy software, databases, and all necessary tools, without any significant business interruption.
Last, but certainly not least, we are deeply committed to implementing state-of-the-art security measures in our solutions, leveraging enhanced cybersecurity practices. We always follow strict data protection policies, comply with relevant security standards, and implement advanced encryption methods to safeguard sensitive financial information. This is especially true for our custom risk management system for a global fintech leader.
Let one of our recent projects speak of our practical experience, as it is a great example of our expertise in action.
Fraud Detection System for a Leading Payment Processing Platform
Business Challenge
One of our long-term Fintech clients, a payment processing company with millions of online transactions per day, faced an alarming rise in fraudulent activity in a short period. In addition to our main tasks for this project, we were tasked to build a powerful ML-based credit card fraud detection solution from scratch, with the function of transaction analysis in real-time.
SPD Technology’s Approach
After an in-depth analysis of the patterns in financial transactions, we decided to design the solution around machine learning algorithms, anomaly detection, and real-time data processing. We built a data pipeline to ingest all transactional data, using advanced data-cleaning techniques to eliminate noise and irrelevant information, ensuring that the ML models were trained on high-quality data. As for ML models, we went with a layered approach to fraud detection, combining supervised and unsupervised learning.
The next step was to design a real-time decision-making engine, able to analyze each transaction in milliseconds. We were able to build a lightning-fast engine that flagged suspicious activities, routed them for review, and, most importantly, didn’t affect legitimate transactions.
Our team integrated our custom credit card fraud detection solution with the client’s payment platform by using RESTful APIs while leveraging Docker for ease of deployment, scalability, and maintenance. We ensured that our system complied with PCI DSS, and incorporated encryption and tokenization. In terms of security, we also integrated a 360-degree risk assessment to detect potential vulnerabilities in the payment ecosystem of our client.
Value Delivered
- Massive Security Improvement: Our solution reduced false positives by 30% without slowing down or blocking legitimate transactions.
- Real-Time Fraud Detection: We delivered real-time transaction processing with under 100ms response times, introducing instant detection and prevention of fraudulent activities.
Ultimately, our fraud protection and payment gateway development company helped the client improve transaction processing and reduce fraud-related financial losses without any negative effect on customer experience.
Conclusion
Machine learning is a potent weapon against credit card fraud because of its capability to scrutinize vast financial data and identify complex fraudulent patterns. Financial card fraud manifests in different forms, from in-person and online scams to identity theft, necessitating sophisticated detection methods.
The journey of using ML for detecting credit card scam involves several stages, including data collection, preprocessing, feature engineering, model training, and evaluation. Different machine learning algorithms and models are employed, each tailored to tackle specific fraud challenges.
Success in spotting fraud with ML depends not just on technical proficiency but also on ethical and privacy considerations. Addressing imbalanced data, interpretability of fraud detection machine learning models and real-time detection capabilities also contributes to efficient scam detection.
In essence, ML for fraud detection signifies a substantial transformation in fortifying transactions across various sectors, including financial institutions and credit card companies. By leveraging data-driven insights and advanced algorithms, businesses and consumers can navigate the digital payment landscape with confidence, knowing they are protected from fraudulent activities.
FAQ
How can machine learning models reduce false positives in fraud detection?
ML models can reduce false positives in fraud detection by learning sophisticated patterns in transactional data and distinguishing between fraudulent activity and legitimate user behavior. Machine learning in fraud detection can achieve this through assessing various features, including transaction history, user behavior, location, and device data. Thanks to techniques like supervised learning with labeled fraud data, anomaly detection, and ensemble methods, systems can flag fewer legitimate transactions as fraud and reduce false positives.
What are the algorithms used for credit card fraud detection?
The following algorithms, along with various ensemble methods, feature engineering techniques, and model evaluation metrics, are employed in credit card scam detection systems to effectively identify and prevent a fraudulent transaction while minimizing false positives.
- Logistic Regression: Used for binary classification tasks, logistic regression models the probability of a transaction being fraudulent based on its features.
- Decision Trees: Decision trees partition the feature space based on feature values to classify transactions as fraudulent or legitimate.
- Random Forest: An ensemble learning method, it combines multiple decision trees to improve detection accuracy and robustness.
- Neural Networks: Deep learning neural networks, including feedforward, convolutional, and recurrent neural networks, learn complex patterns in financial data for fraud monitoring.
- Isolation Forest: An unsupervised learning algorithm, isolation forest isolates anomalies in transaction information by partitioning the feature space.
- K-means Clustering: Used for grouping transactions into clusters, k-means clustering identifies outliers as potential fraud instances.
How can machine learning detect credit card fraud transactions?
ML algorithms assess historical transaction information to spot patterns and anomalies associated with fraud schemes. Features such as transaction amount, location, time, merchant, and customer behavior are extracted and used to develop models. Supervised learning models are trained on labeled data (fraudulent and legitimate transactions) to learn to distinguish between them. Unsupervised learning models spot deviations by identifying transactions that vary significantly from normal behavior. Blended strategies combine supervised and unsupervised algorithms to improve accuracy of detection.


