For virtually any business that needs to collect revenue at scale, billing is one of the most crucial financial processes that can either improve and expedite cash flow management or significantly impact customer satisfaction, revenue leakage, and payment delays.
As market dynamics evolve, more businesses are turning to custom billing software to address their unique business needs and stay competitive. Driven by the goal of avoiding such negative consequences in their billing processes, companies across industries opt to create custom billing software from scratch and fully align the newly created solution with their business operations.
This article will help you do precisely this: gain a firm idea about the meaningful aspects of developing custom billing software and the kind of interactions you, as a client, should establish with billing software developers to make sure the solution aligns with your business goals.
Decide on the Type of Your Billing Software
Before discovering how to make billing software step-by-step, you have to decide on the type of the billing app you need. Next, it will become a foundation to effectively compile the list of required features. Determining the type of the billing application that best fits your needs will also help your billing software provider tackle your business needs more proactively.
Below are three basic types to choose from when planning a billing system, but keep in mind that the functionalities of each kind may overlap as well:
- Custom invoicing software is a software solution focused on generating invoices and related reports.
- Subscription (recurring) billing software is an application that enables automatic billing for complex billing scenarios in accordance with a predefined scenario throughout the customer lifecycle.
- Time and expense tracking and billing software is an application that provides expense management and time tracking for client projects, as well as automated invoicing based on time or flat fees.
When comparing off-the-shelf solutions and custom billing software, it’s important to weigh their advantages and limitations. Off-the-shelf billing software offers a ready-made, general-purpose solution with standard features, making it quicker and more cost-effective to deploy. However, while using off-the-shelf billing software can be a fast solution, it may lack the adaptability needed for specialized workflows or evolving business requirements. In contrast, custom billing software can be tailored to your specific business needs, which offers flexibility in invoice templates, workflows, and branding. This tailored approach ensures the software aligns with unique operational requirements for more efficient financial processes. However, advanced features or customizations in billing software can be expensive compared to standard options.
Several factors contribute to the choice and cost of billing software, including the complexity of required features, integration needs, and scalability. Customization, advanced features, and ongoing support also contribute significantly to the overall cost of billing software development and should be considered when budgeting for your project. Additionally, consider the pricing models supported by each billing software type. Flexible billing structures, such as flat-rate, usage-based, and hybrid pricing models, are essential for accommodating business growth and diverse customer needs. Choosing a system that supports your preferred pricing models will ensure your billing processes remain scalable and customizable.
Custom billing software development costs typically range from $45,000 to $350,000 or more, depending on factors such as scope, complexity, and team size. The size and location of the development team can also influence the overall cost of custom billing software development.
Define System Requirements
Any complex software development project starts with defining the requirements for the system to be built, and custom billing software development is no exception. When defining system requirements, it’s essential to follow key steps such as gathering stakeholder input, analyzing business processes, and prioritizing features to ensure a secure, scalable, and efficient billing system. Let’s now review the different groups of requirements associated with your billing system’s main functional capabilities and identify what a development team should pay attention to when dealing with them.
Understanding business requirements and specific requirements is essential to ensure the software meets its intended purposes and aligns with organizational objectives. You need to evaluate both current and future user and business needs before starting development, as capturing requirements can be challenging due to the complexity and diversity of business requirements.
As part of requirements definition, it’s crucial to set up and configure workflows and integrations, such as CRM integrations and billing automation, to ensure smooth operation and automation in your billing software.
Invoicing
First, one should categorize and describe all the projects and services your business offers, and allow for the addition of new product and service categories. Next, it is essential to define the requirements for issuing invoices to bill for these products and services.
Also, keep in mind that when defining invoice-related requirements, it is important to specify the formats your invoices must be issued in. Besides, the invoicing software user must be able to use customizable invoice templates to modify existing invoices.
Customizable invoicing features allow users to customize templates, branding, and custom workflows, ensuring flexibility to adapt invoicing processes to specific business needs. Users can customize invoicing workflows to match their business processes, enhancing efficiency and integration.
Flexibility in invoicing features is crucial, enabling businesses to support various payment methods, recurring invoices, and multiple currencies. Mobile invoicing capabilities are also essential, allowing users to handle tracking payments and managing invoices directly from their smartphones, improving convenience and speeding up payment cycles. Mobile features enhance the overall user experience by enabling on-the-go invoice management.
Regarding invoice delivery to your customers, the requirements must list all available channels, such as a customer portal, SMS, email, and any others. Fast delivery and processing of invoices should be prioritized to improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Additionally, it may be helpful to enable invoicing automation, with options to specify a date or a date range.
It is also important to ensure that the billing software securely manages customer details. Billing software stores and tracks sensitive customer information, including contact details and payment history. To protect this data, the software should implement encryption, data protection measures, and permission controls. Compliance with local data protection regulations is essential to safeguard customer details and maintain regulatory standards.
Recurring Billing and Subscription Management
To support subscription billing for products and services billed multiple times, your solution must allow recurring invoices across modifiable billing cycles. Also, if the nature of your business requires the ability to work with subscription plans, this functionality should also be outlined in your SRS document. Implementing a subscription management capability supports automated billing for a series of billable events within one of the usage scenarios (or subscription plans) that you offer.
Your system must support both recurring and one-time payments to provide flexibility across various billing scenarios. Additionally, the system should handle free trials or free plans, allowing customers to experience your service before committing. Adaptability is crucial, as your billing software must easily accommodate different subscription plans and support changes, including plan downgrades, upgrades, and cancellations. This ensures accurate billing and synchronization with customer data as users move between plans.There are two things to pay attention to here: firstly, your system must bill only for the period that the customer has been using your services. This means that the application must run the corresponding checks. Secondly, all the subscription packages must be completely modifiable – you must be able to update or expand them at any time and then automatically bill for any new billable events added. Such subscription management and billing functionality is part of the BlackHawkNetworks (BHN) aggregated merchant portal (AMP) that we developed.
Tax and Compliance Regulations
You can conveniently incorporate tax calculation functionality into your automated billing software to calculate any taxes due on the sale of the products or services your invoices cover. Tax compliance is a critical component of billing software, ensuring that your system supports industry standards and regulatory requirements for accurate financial reporting across different geographic regions.
To do so, you should indicate this as a requirement, stating that your tax calculation module must calculate taxes for all your products and services for all your relevant jurisdictions while taking into account any applicable exemptions and thresholds. One must be able to easily configure the taxation rules to keep them up to date. In this way, we have created tax calculation functionality for an Israeli real estate company with dynamic recalculation and multiple parameters embedded. Also, mind that compliance with industry-specific regulations and security standards can increase the cost of developing custom billing software.
User Role Hierarchy
Just like with any other solution, your SRS document must describe the user hierarchy for your custom billing software to support finance teams.
More specifically, your development team must list all user roles and specify the corresponding permissions for each role. Among other things, this means indicating which user roles will have authority over bank transfers and accounts. For example, your user hierarchy could include:
- Administrator, who can manage user access, assign roles to new users, and reassign roles to existing users.
- Accountant, who manages accounts, cash flow, overdue payments, and the collection of funds.
- Sales manager, who monitors the payment status of key accounts.
- Configuration engineer, who manages the billing workflows and performs overall system maintenance.
- Regular users, whose rights should be defined individually, depending on your business specifics.
Please note that if your business has any resellers, this role should be envisaged as well. Most likely, the Reseller role should include the ability to add customers, create professional invoices, and collect payments. In this regard, your authorized staff must be able to supervise reseller-related invoicing and process payments. At the same time, your solution must also calculate any related taxes due to you.
Other Important Requirements
Some other requirements should be included in the SRS document. If you work with multiple currencies, you must indicate this as well: list all the currencies you will use and add the ability to expand the list later. Billing software should support multiple payment methods, including credit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets, to provide flexibility and enhance customer experience. The software should allow for customizable reports in various formats to meet diverse business needs. Also, clearly list and describe all automated billing and payment processing tasks you want to implement, such as sending payment reminders and generating invoices.
Shortlist the Necessary Software Features
Based on the business needs and related requirements you’ve defined, your provider of custom billing software development services will come up with a list of the functional capabilities your solution will include.
There are several ways to implement billing automation, such as deploying custom-built solutions or choosing off-the-shelf software, each offering different approaches to streamline your financial processes and improve operational efficiency. You should thoroughly discuss this list with them, use your knowledge of your business domain and situation to augment its contents, and agree on the listed functions.
The functions that a full-blown software solution would likely include are:
- Invoice and billing management: functionality that allows generating invoices from scratch and based on existing invoices, both manually and automatically.
- Automated billing and related payment processing: functionality that allows you to send invoices to customers using different channels and monitor the payment status of customer accounts.
- Product and service catalog: a comprehensive listing of all your products and services you need to issue invoices and bill for, which allows you to easily select such products or services and add them to invoices.
- Subscription management and recurring billing: a functional capability that automatically bills a customer during their lifecycle in accordance with a selected subscription package, or performs automatic billing for a recurring service.
- Tax and compliance: functionality that calculates all the taxes that are due to be paid from the sales your billing operations are associated with, including the sales tax, VAT, and any other taxes that you are to pay in your jurisdiction.
- Notifications and reminders: functionality that allows automatically sending various notifications and payment reminders to specific target audiences at specified dates, or when some specified conditions are met.
- Transaction consolidation: a capability that supports multiple payment methods and merges multiple purchases of products and services into a single invoice.
- Management of delinquent accounts: functionality that makes it easy to check payment status, identify overdue invoices, and send relevant payment reminders or take some other appropriate action.
- Reporting: a capability that allows finance teams to generate collection reports and tax summaries and manage expenses.
- Reconciliation of subscription and non-recurring charges: this feature enables seamless integration of charges within the billing system and integrated accounting software, ensuring accuracy and transparency in financial transactions.
Choose the Right Technologies
At the next step of the billing software development process, choose the technology stack you need for developing custom billing software solutions. Our practical experience in fintech software development suggests that the following tools can be strategically selected to build a robust and secure billing solution.
- Programming language: Java.
The Java programming language provides a secure and scalable foundation for custom billing software, crucial for handling sensitive customer data and accommodating the growing transaction volumes inherent in fintech applications. - Backend framework: Spring Boot.
Spring Boot is a widely adopted framework that helps the development team build microservices-friendly Java-based solutions. The Spring ecosystem provides comprehensive features, such as data access, transaction management, and data security, all of which are crucial for fintech applications. - Frontend framework: Thymeleaf and React.js.
Thymeleaf is a server-side templating engine that integrates seamlessly with Spring Boot. If a more interactive user interface is desired, React.js can be integrated with Thymeleaf to build responsive components. - Message queue: Apache Kafka.
Apache Kafka is a distributed event streaming platform that can be employed for asynchronous communication between components of the billing systems. It ensures reliability, fault tolerance, and real-time payment tracking, which are crucial for financial transactions. - Database: PostgreSQL.
PostgreSQL is a robust open-source relational database often used in a billing system, known for its ACID compliance and support for complex queries. It integrates seamlessly with Java via JDBC and Hibernate, providing an excellent foundation for securely storing and retrieving sensitive financial data. - AI/ML Integration: Python and TensorFlow/PyTorch.
Python is widely used for AI/ML development due to its rich ecosystem of libraries, including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn. These libraries provide tools for building, training, and deploying machine learning models. Models can be deployed via REST APIs built with frameworks such as Flask or FastAPI, and these can be integrated with the main Java backend.
We used Python for AI/ML development for one of our clients. Our team developed a Python pipeline that efficiently classifies item lines in invoices. Using AWS Textract, the tool first extracts the text and tabular data from PDF documents. To fine-tune the functionality, we leveraged NLP techniques, text classification, and text embeddings, the pipeline then accurately categorizes item lines. As a result, we saved operational time for a client and reduced manual effort.
Implementing Invoicing Logic
The ability of custom billing software to seamlessly meet your business needs hinges significantly on how thoroughly and meticulously you implement the invoicing logic required in your case. That is why it makes sense to spend more time defining the logic of your invoicing software and to ensure none of the critical steps are omitted or downplayed.
We would suggest the following checklist to ensure the logic implemented in your software optimizes your billing workflows:
- Specify the pricing structures, discounts, and tax rates for each product or service offered by the business.
- Define the tax regulations applicable to the business. Make sure the tax rates are applied across all jurisdictions in which you operate.
- Specify how the taxes should be calculated and applied to your invoices.
- Specify all required automated billing features to streamline payment processes and reduce manual effort.
- Detail the subscription billing packages that the system needs to support.
- If this makes sense, implement billing calendars with varying timeframes, such as once a month, once every 3 months, or once a year.
- Implement automatic recurring invoices.
- Implement flexible invoice generation.
Following this detailed invoicing logic implementation checklist, we have designed an invoicing & billing subsystem for Pie Insurance, one of our major customers in the Insurtech domain. The billing subsystem we developed allows the creation, updating, and tailoring of billing plans, including specialized payroll reporting plans. It also facilitates the recording, tracking, and reporting of premium billing, payment plans, and received payments.
Furthermore, our solution empowers Pie Insurance to accurately monitor and report on each policy’s equity and automatically execute policy cancellations based on equity calculations. Addressing the nuanced regulatory landscape, where each U.S. state has distinct cancellation-related rules, the system adeptly tracks non-payment cancellations.
Integrate a Payment Gateway
Now, let’s proceed to discover how to create billing software from a technical standpoint and integrate it into your financial operations. For your software to be fully functional, you need to integrate it with a payment processing gateway, and optimally, with customer relationship management and accounting software.
Usually, a billing system starts to process payments because billing events such as invoice generation or subscription renewal occur according to a predetermined schedule. That’s why billing software should include a payment API client (a software component that interacts with the API by making HTTP requests to API endpoints) to enable communication with a payment gateway. When it comes to payment gateway integration, it’s best to opt for a RESTful API-based approach. By leveraging the payment gateway’s API, we can establish a direct communication channel between the billing system and the payment processing service to transmit customer data and maintain data security. This method ensures real-time data synchronization and facilitates a smooth flow of information during transactions.
Follow a step-by-step guide to integrating a payment gateway with our expert article.
Also, be aware that maintaining consistency of payment details between the billing system, ERP systems, and the payment gateway is crucial. The proven way to address this challenge is to implement a reliable data synchronization mechanism to ensure accurate and up-to-date information on both ends. With these specific issues of integrating a payment gateway into a custom software, you are welcome to follow the next step-by-step algorithm:
- Establish API credentials
- Building the API client
- Implement secure communication
- Integrate support for multi-currency payments (e.g., credit cards, bank transfers)
- Incorporate error handling mechanisms
- Ensure data consistency
- Perform user acceptance testing in a sandbox environment
Build Secure a User Authentication Mechanism
Securing user access to an application that is used to control financial flows and the related confidential information is one of the Fintech development challenges that needs to be solved only reliably enough.
To ensure financial data security in this case, one should settle for Two-Factor (2FA) or Multi-Factor authentication only, and pay special attention to the selection of a truly reliable second factor your employees would be comfortable with. It makes sense to look in the direction of the more user-friendly biometric methods like, for instance, Iris Identification or Voice Identification, or advanced Face Recognition. In the latter case, one should check whether the solution offered has robust anti-spoofing protection against the sophisticated modern types of fraud, like, for example, 3D masks.
Ensure User-Friendly Design
Just like any business system, your billing software should have an intuitively user-friendly GUI. As the GUIs of high-scale billing software solutions often provide access to a large number of diverse functions, this may not always be an easy goal to achieve for their developers. For you to have better odds of having user-friendly GUI developed for your billing application, you should opt for a provider of bespoke software with experience in developing GUIs for feature-rich, enterprise-grade applications.
Below are some of the best practices to design user-friendly automated billing software:
- Implement a clear and consistent navigation structure to make it easy for users to locate essential features and functions.
- Design an uncluttered customer portal dashboard that provides a quick overview of key billing metrics and alerts.
- Provide real-time, contextual feedback for user actions. Use tooltips, notifications, and error messages to guide users through invoice creation and address any issues promptly.
- Streamline data entry with smart form design. Use auto-fill, drop-downs, and date pickers to reduce manual input errors.
- Minimize risks and ensure secure transactions with robust data security and compliance measures in billing software, providing peace of mind for both finance teams and customers.
- Reduce friction in the checkout and payment processes to lessen payment reconciliation delays and improve customer satisfaction.
Keep Fintech Compliance Regulations In the Spotlight
Your billing software must comply with the main security and payment processing compliance regulations, including PCI DSS, SOC 2, and PCD. Before the start of your project, you should become thoroughly familiar with these regulations and discuss with your software provider how they will ensure compliance.
Please also make sure that your provider of choice can conduct the PCI DSS-mandated security penetration testing of your application. They must be able to test your collusion’s abilities to counter cyber attacks (SQL injections, ORM injections, and others), securely transmit credentials, securely and compliantly manage passwords, etc.
Ensure Compliance With Financial Reporting and Accounting Standards
In addition to the required security compliance, you are expected to ensure the billing system complies with the Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), and Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606.
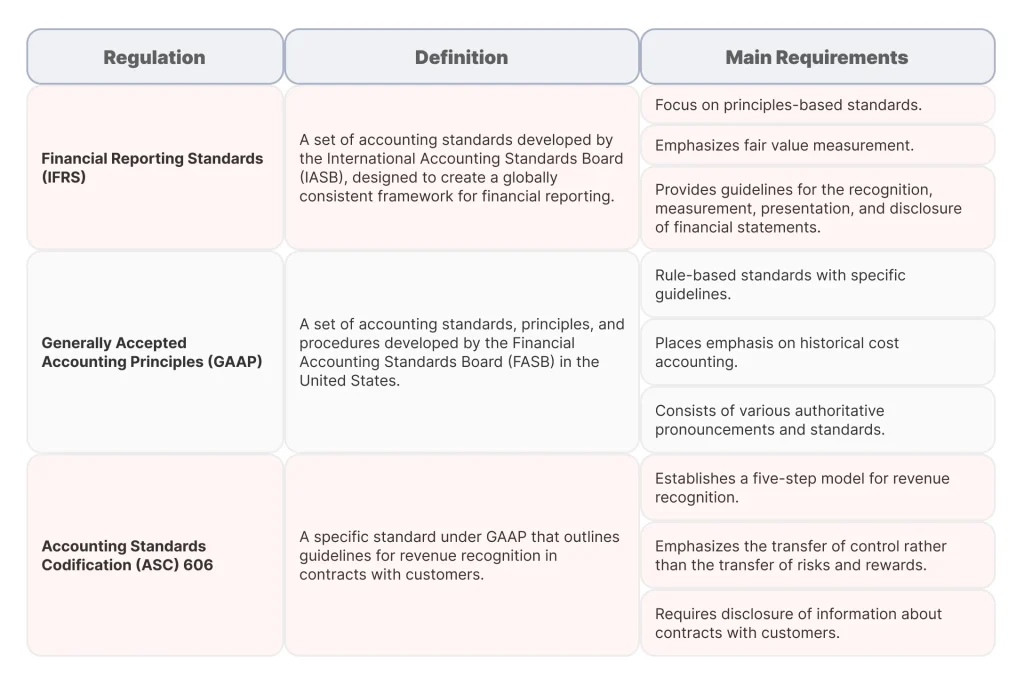
The IFRS and ASC 606 standards aim to make sure that revenue is recognized only after it has been earned by meeting a contractual obligation. This requirement can be tricky to meet, for example, with complex subscription plans that require advance payments. For example, IFRS compliance requires that your system must allow you to:
- Identify the one or more contracts you have with the customer.
- Identify the performance obligations stated in this contract.
- Determine the price of the transaction.
- Recognize revenue when the company meets its obligations.
- Allocate the performance price to the performance obligations.
GAAP compliance helps recognize revenue for bill-and-hold transactions (whereby the product is sold but not delivered immediately): revenue recognition can occur only when a condition is met.
Because of the great importance of financial reporting and accounting standards, you must gain a good command of them and reflect their requirements in your automated billing system.
Keep Fintech Compliance Regulations In the Spotlight
Your billing software must comply with the main security and payment processing compliance regulations, including PCI DSS, SOC 2, and PCD. Before the start of your project, you should become thoroughly familiar with these regulations and discuss with your development team how they will ensure compliance.
Looking for practical tips on how to become PCI DSS-compliant?
See our comprehensive PCI DSS compliance checklist.
Please also make sure that your provider of choice can conduct the PCI DSS-mandated security penetration testing of your application. They must be able to test your collusion’s abilities to counter cyber attacks (SQL injections, ORM injections, and others), securely transmit credentials, securely and compliantly manage passwords, etc.
Conclusion
In summary, this article highlights key considerations in billing software development, including understanding business needs, compliance requirements, and the importance of partnering with experienced tech vendors. Billing applications represent complex software systems with intricate functionality that are heavily influenced by a range of regulations and must comply with them.
Correspondingly, if you wonder how to make billing software, you should first gain a deep understanding of your billing-related business needs and compliance matters. It would also be wise to partner with a tech vendor and leverage their fintech-specific expertise to build a robust solution that integrates with your accounting tools. Looking ahead, adopting a proactive, strategic approach to billing software development is the best way to avoid common pitfalls and support your business growth.At SPD Technology, we are always delighted to share our expertise in automated billing software development with those looking to improve or automate their financial processes. You are welcome to talk to our experts.
FAQ
How to make billing software from scratch?
To develop billing software from scratch, you should start by deciding on the type of software you need. Depending on the type, you will be able to define system requirements, including but not limited to invoicing platform, subscription management, user role hierarchy, and compliance requirements. Then, shortlist the necessary features and, based on them, develop the UI for your future solution. Partnering with a billing software development vendor is the wisest decision along this way, since the tech-savvy software developers would be able to support you with their technical knowledge, quality assurance, and expertise competently. Ongoing maintenance and technical support are necessary after deployment to manage issues and updates.
How to create your own billing system?
Gain an understanding of your business needs and approach a custom software development company with enough experience in your niche to create an SRS document and get the project underway. Building a billing system in-house can be complex and resource-intensive, requiring your team to handle compliance, security, and ongoing maintenance. Custom billing software development requires deep technical resources, long development cycles, and constant updates to meet compliance standards. The development timeline can vary significantly depending on feature complexity and project size. Successful implementation involves thorough testing to validate functionality, performance, and security, helping you find and address any problems before deployment.
How to succeed in creating custom invoicing software for shops?
One should approach an experienced billing software development company that develops custom solutions and provides full-cycle software development. You should help their business analysts gain insights into your business context and needs so they can architect and develop the solution you need. A well-designed billing platform provides your organization with the freedom to make strategic decisions without being constrained by technical limitations or outdated systems. In retail environments, integrating point-of-sale (point) systems and ensuring robust back-office (office) billing management are essential to streamline transactions and support operational efficiency. Custom billing software can save money in the long run by eliminating monthly fees associated with generic software. Best practices include designing for scalability, security, and user-friendliness, and focusing on core features like automated invoicing and flexible payment options.



