Being the core data for any business, master data represents the critical information that an organization relies on to operate its business and make strategic decisions. Despite its critical importance, many organizations struggle with creating a master data management strategy and implementing it effectively. According to the research by Tamr, without a master data management strategy (MDM), data practitioners spend up to 80% of their time cleaning and preparing data, instead of focusing on other critical tasks.
Additionally, without an efficient master data management strategy in place, there is always a risk of data silos, major inconsistencies, and overall lack of efficiency across departments, that harm a winning decision-making process. That’s why in this article, we explain what makes an effective Master Data Management (MDM) strategy, overviewing the process for its development and listing the necessary tools for its further implementation.
The Importance of a Master Data Management (MDM) Strategy
Master data is one of the most valuable business assets of an organization, as it represents such critical information as customer, product, and supplier details, as well as information on the internal processes. A thought-out MDM strategy, a part of a broader data management framework, ensures that this core information remains accurate, consistent, and accessible across all business systems and processes.
Unlike the transactional data management strategy of day-to-day data, MDM focuses on unifying, cleaning, and controlling the data entities that impact multiple departments and workflows. The main goal of MDM is to create a single source of truth, a highly reliable and completely consolidated version of critical data.
Business Benefits of an MDM Strategy
By committing to the quality of master data, companies ensure sustainable growth and gain the following advantages:
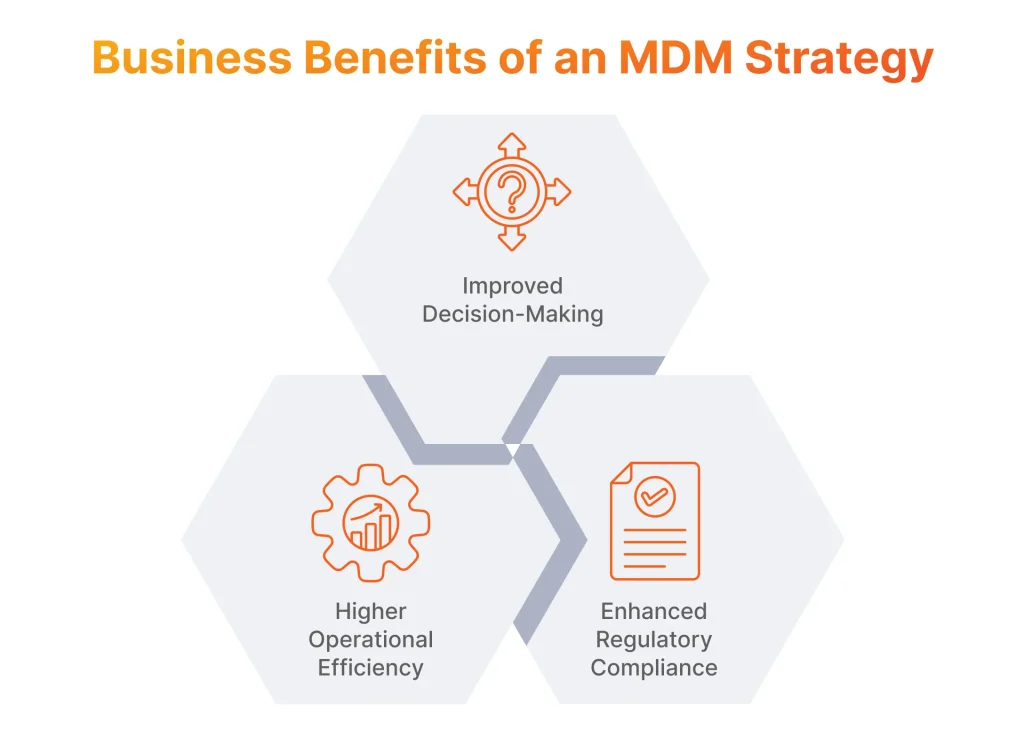
- Accurate Decision-Making: With access to clean, consistent data, leaders can confidently make data-driven strategic decisions. Centralized master data helps to eliminate discrepancies and conflicts across systems.
- Boosted Operational Efficiency: By standardizing data from the different departments, organizations can leverage quick access to reliable data, allowing their employees to complete tasks more efficiently and productively.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: Robust MDM practices allow companies to track and audit data usage and lineage, managing sensitive data responsibly and meeting data privacy regulations including GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“I believe that a master data management strategy isn’t about just managing critical data, but rather about massive optimization of every single part of an organization and reducing the manual workload. Recently, my team helped to integrate an MDM strategy for our long-term client, resulting in an impressive 50% reduction in data-related errors and a massive improvement in customer response times.”
Essential Components of a Master Data Management Strategy for an Enterprise
To obtain an effective strategy, it is crucial to foresee and dwell on several interconnected components that ultimately ensure the accuracy, security, and overall accessibility of data across the organization. These components for an enterprise data strategy as related to master data include the following.
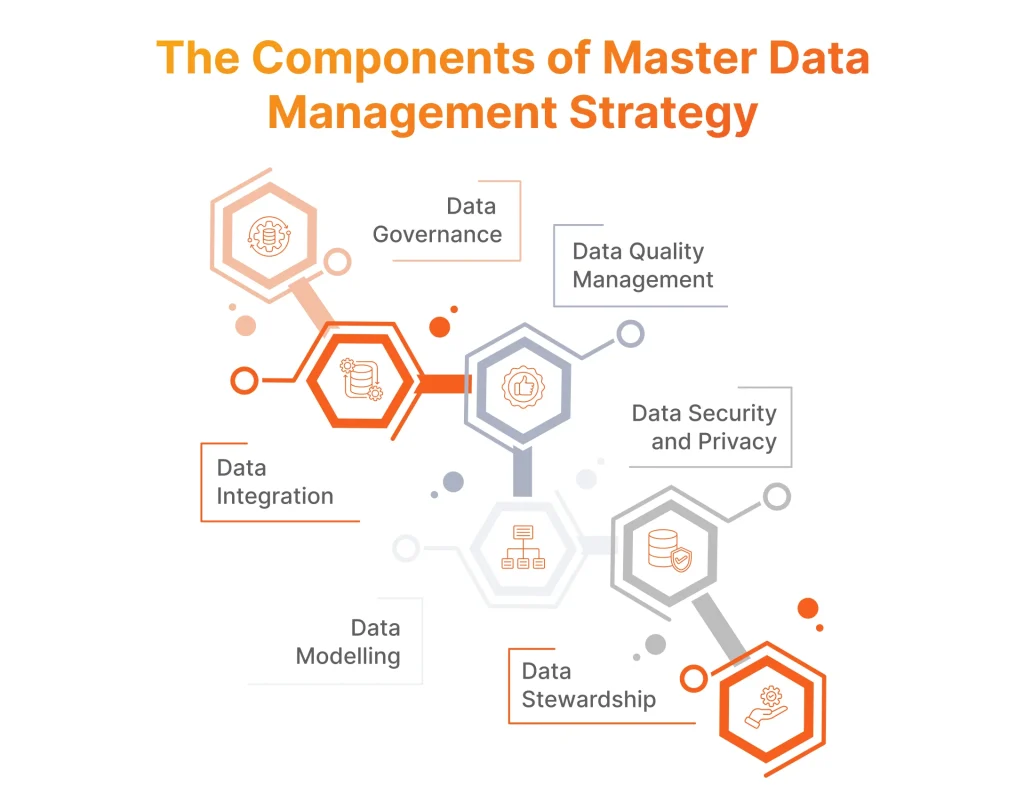
Data Governance
Governance serves as a foundational element of the master data management strategy for an enterprise, establishing the principal policies, processes, and standards of data management. It ensures clear and understandable data usage responsibilities across departments and outlines roles for data stewardship, data quality, and compliance.
Data Quality Management
Being an essential part of an enterprise data management process, data quality management is required for maintaining data accuracy, reliability, and completeness, and includes implementing specific tools and processes to monitor, cleanse and validate data. Securing high-quality data is a critical condition for achieving a “single source of truth” aspect of MDM, needed for accurate decision-making.
Data Integration
It consolidates data from entirely different sources into a unified system and unlocks the data flow across the departments and applications. Data integration is achieved through techniques like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and API connectivity, enabling a holistic view with analytics and reporting functionality.
Discover the importance of data integration, as we discuss this topic more closely and emphasize the key benefits and challenges in our dedicated article.
Data Security and Privacy
Being a core component of any MDM strategy, it is vital to plan the implementation of encryption, and access controls, as well as conduct regular audits to protect sensitive information from any unauthorized access or breaches.
Data Modeling
It is important for structuring data in a specific way that supports the critical objectives of organizations, as well as facilitating integrity and consistency. Efficient data models should represent the essential entities and relationships, simplifying retrieval and usage of information for departments.
Data Stewardship
It is required for assigning responsibilities in overseeing and managing information. Dedicated experts, called data stewards, control the adherence to data management policies and make sure that all data-related issues are quickly resolved.
Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“An efficient MDM strategy has the synergy of all the above-mentioned components. Data governance provides a specific set of rules, data quality management guarantees the highest level of accuracy, data integration consolidates all of that information, and data modeling provides structure. Data security is aimed at introducing processes to protect data access, while data stewardship enforces these processes across the entire organization.”
Organizational and Cultural Aspects of Efficient Master Data Management Strategy
Developing MDM strategies requires changes in both a company’s organizational and cultural levels to truly embrace the changes and effectively implement the strategy. We, at SPD Technology, have extensive experience in data management consulting, so here is what we think is important to change for MDM strategy implementation.
Organizational Aspects
- Leadership Support: positioning MDM as the highest priority for leadership shows employees that proper data management is valuable for the company. When neglected by leaders, MDM strategy implementation will most likely fail due to fragmented efforts and minimal engagement of the employees.
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: typically, the MDM strategy involves multiple departments that need to synchronize data to operate without disruptions. If the proper level of collaboration is missing, some departments can become siloed, providing inconsistent outputs and leading to overall inefficiency.
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities: defining roles help stakeholders obtain accountability and ownership of master data. Any uncertainty in roles may lead to confusion, lack of accountability, and poor data management.
- Established Data Governance Framework: having this framework is required for setting standards, policies, and processes to know how to manage master data. Without governance activities, data management can become chaotic with inconsistent definitions and quality of data, leading to risks in security.
- Ensured Integration with Existing Processes: this is required to ensure that master data management techniques become an organic part of the organization, improving data quality across an entire organization. When MDM is treated as an isolated initiative, employees may not fully support it and by this not leverage all possible benefits.
Cultural Aspects
- Data-Driven Culture: it is very important to encourage employees to view data as a basis for informed decision-making. Without this foundation, employees may underestimate data quality and make uninformed decisions.
- Change Management: there can always be some resistance, or outright rejection to change in your organization. To fully support the MDM strategy, it is necessary to take action on addressing new data practices and break down to employees all the details that may concern them.
- Continuous Improvement Mindset: data practices always require regular updates and evaluation to match the needs of an organization. To develop this mindset among employees, it is necessary to regularly communicate successes and lessons learned from MDM strategy improvement initiatives. It will also be effective to use feedback loops to refine processes and demonstrate that suggestions lead to tangible changes.
Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“In addition to obtaining leadership support and driving smooth collaboration between departments, don’t forget to involve middle management as well, setting them as data champions. The middle managers are the ones who bridge the stakeholder’s vision with daily operations, helping teams to embrace the MDM approach.”
Developing a Master Data Management Strategy
Once the foundation with cultural and organizational adjustments is in place, an organization can move on to developing a data management strategy. Here are the essential steps of this process:
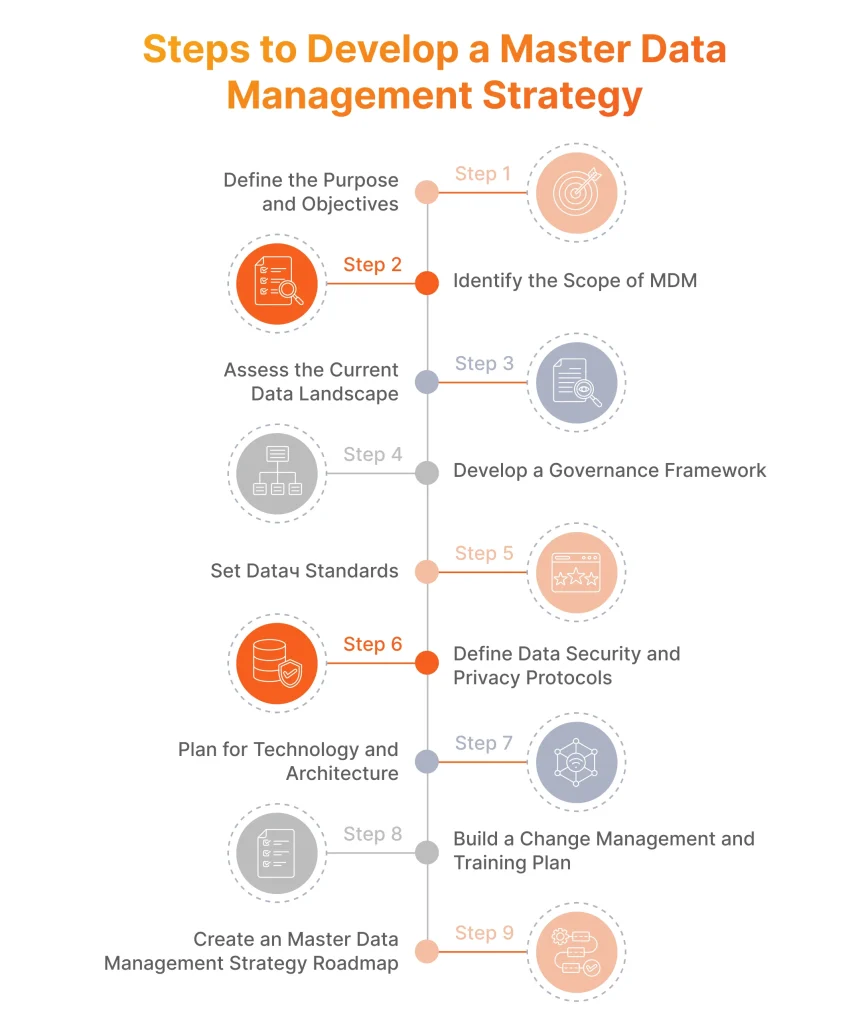
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Objectives
It will be a good idea to start by aligning your MDM strategy with long-term business goals. This includes having specific, tangible metrics regarding data quality improvement or lowering operational costs. It is also important to identify specific challenges of your organization like data silos and describe how MDM can address them. As a result of this step, you should receive a holistic Executive Summary with clarifications on the purpose and value of the MDM initiative.
Step 2: Identify the Scope of MDM
After you get the summary, it will be time to determine specific data domains to be managed under your MDM strategy, which may include such types as product, customer, or supplier data. Your scope may cover the entire company, or cater to certain departments. It also should consider dependencies in domains and business functions. The resulting output of this step is Scope Definition, which clearly specifies what areas and data the MDM strategy will address.
Step 3: Assess the Current Data Landscape
Existing master data should be audited to make a conclusion on its quality, consistency, and accessibility. This is achieved by involving stakeholders from various departments in finding possible issues and requirements. At this step, you should have a Data Landscape Analysis for potential challenges and ways for improvement.
Step 4: Develop a Governance Framework
The framework is required for structuring data management, establishing data stewards, and assembling councils for data-related decisions, as well as policies for data ownership, quality, and lifecycle management. A resulting document, Data Governance Framework, should contain detailed roles and responsibilities, with outlined authority for resolving data issues.
Step 5: Set Data Quality Standards
The data accuracy, completeness, consistency, and some other metrics should be clearly defined, while the monitoring processes should be implemented with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). The Data Quality Management Plan is what you will have on this stage, which will outline the critical data standards.
Step 6: Define Data Security and Privacy Protocols
While working with data, security is always of the utmost importance, so at this step, potential security risks should be identified and prevented. Your organization’s privacy protocols must comply with the latest security standards and regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, so you will receive a Data Security and Privacy Strategy at this stage to achieve this goal.
Step 7: Plan for Technology and Architecture
A wise choice of a tech stack can be a key to the overall success of an MDM strategy. Based on the specific needs, the choice between cloud or hybrid architectures should be made. The MDM platform of your choice should easily integrate with your existing systems and support scalability, as your business grows. This step results in a Technology and Architecture Plan that defines specific tools and integrations for your MDM strategy.
Step 8: Build a Change Management and Training Plan
This plan includes a detailed communication approach that emphasizes the benefits of the MDM program and helps employees to grasp completely their roles in data governance. With a heavy involvement of stakeholders, this stage results in a Change Management and Training Plan with requirements for successful implementation.
Step 9: Create a Master Data Management Strategy Roadmap
Finally, a detailed MDM strategy roadmap should be created, with a precise list of actions breaking down the strategy into manageable chunks with milestones, timelines, and responsibilities. This comprehensive MDM strategy roadmap will ensure the full alignment of your data initiative across the entire organization.
The opportunity to develop a data strategy step-by-step is one of the numerous advantages of strategic technology consulting.
Discover more business benefits in our featured article!
Master Data Management Strategy Template
To follow each of the steps confidently, consider using an MDM strategy template example, highlighting key elements to elaborate on.

MDM Strategy Tools and Technology Infrastructure Specifics
Building an effective MDM technology infrastructure has its own set of unique challenges. We know how to overcome these hurdles while maintaining data quality, so in this section, we will discuss key considerations for this aspect of MDM, as well as the most prominent tools and technologies.
Key Considerations for Building MDM Tech Infrastructure
- Interoperability: it is required for smooth operations across systems, especially legacy ones. An effective MDM infrastructure requires middleware or integration platforms to bridge gaps between systems of different generations and ensure uninterrupted data flow.
- Scalability: for any growing organization, the expansion of the amount of data is constant, so your MDM infrastructure should be ready to accommodate those needs. Modular design, as well as cloud-native or hybrid platforms, are common solutions for providing scalable storage while scaling specific components when necessary.
- Security and Compliance: it is mandatory to use tools with features like encryption, multifactor authentication, and access controls. Each component of your infrastructure should comply with the latest requirements like GDPR and CCPA to fully maintain data integrity and prevent any possible regulatory risks.
- Real-Time Capabilities: some businesses require real-time or near-real-time data integration and processing for lightning-fast decision-making capabilities. Leveraging in-memory databases and event-driven architectures allows this, providing systems with instant update capabilities, as the new data arrives.
- Cost-Effectiveness: for optimizing expenses while maintaining peak performance, striking a balance between on-premises and cloud solutions is necessary. Some enterprises choose going beyond the basic cloud computing infrastructure benefits and implement a hybrid approach storing critical information on-premise for the sake of a more secure and effective MDM strategy
- Overall Infrastructure Benefits: meeting all the above-mentioned considerations helps companies not only deal with current challenges but also set a strong foundation for future growth and more strict data governance over time.
With these specifics of MDM infrastructure in mind, let’s overview the tools and platform that form it.
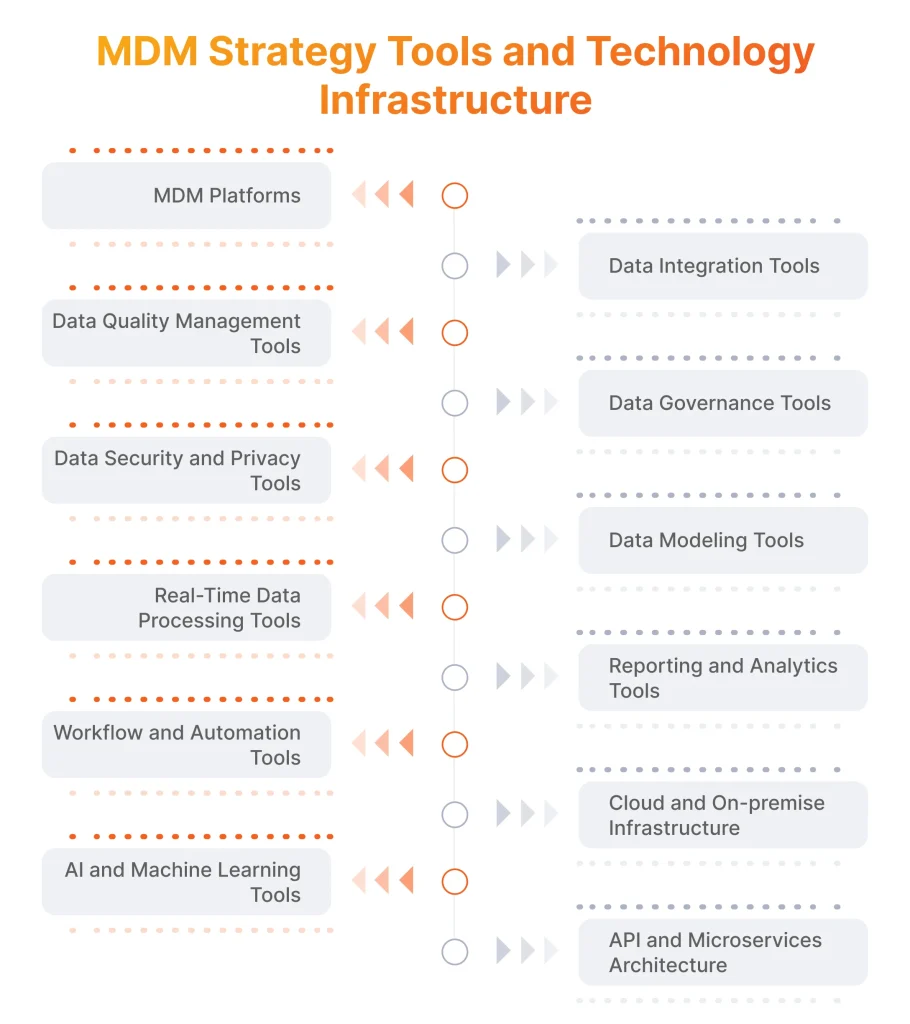
1. MDM Platforms
The top market solutions include MDM, SAP Master Data Governance, and IBM InfoSphere. All three help businesses to centralize data management, and data governance, as well as support multiple data domains. They all include workflow management, hierarchical data handling, and role-based access control, typical features for modern MDM Platforms. While selecting a solution for your particular case, pay close attention to scalability, real-time update support, customization for domain-specific workflows, and data integration capabilities.
2. Data Integration Tools
Speaking of data integration, the most prominent solutions to consider include Talend, Informatica PowerCenter, and MuleSoft. These tools integrate data from various sources into an MDM platform by leveraging extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes with the full support of both batch and real-time synchronization. In the process of making a choice of the right tool for you, consider the most suitable processing mode, pay attention to API support, and learn about the advanced data transformation features for complex data formats.
3. Data Quality Management Tools
Informatica Data Quality, Experian Data Quality, and Trifacta are the leading solutions on the market for this category, as they ensure the accuracy and standardization of data. When you make your selection, it makes sense to double-check whether the tool offers automated data cleansing, and profiling features and whether it can easily connect with governance tools to enforce the highest quality standards.
4. Data Governance Tools
To leverage features like stewardship, auditing, and policy management, you should consider solutions including Collibra, Alation, and Informatica Axon that help enforce data policies. While choosing the right solution for you, make sure the potential option includes support of the role-based access and policy enforcement features, to maintain data quality and compliance, with audit trails to track data changes for accountability.
5. Data Security and Privacy Tools
IBM Guardium, AWS KMS, and Symantec DLP offer the most interesting tools on the market, that provide encryption, access control, and extensive data monitoring features. When making a selection, however, look for some additional features like robust encryption of both at-rest and in-transit data, as well as data masking and role-based access with audit logs.
6. Data Modeling Tools
Modern solutions like Erwin Data Modeler and SAP PowerDesigner help to define the relationships between master data entities to achieve consistency across the company. While making the right decision here, it makes sense to pay close attention to features including entity-relationship mapping, version control for model changes, and metadata management.
7. Real-Time Data Processing Tools
In this category, the most notable solutions are provided by Apache Kafka and Google Cloud Pub/Sub, as they enable continuous data updates across systems in real-time. Whatever option you choose, it should offer low latency to support real-time operations, be scalable enough to handle high data volumes, as well as include a fault tolerance feature to easily recover from any interruptions.
8. Reporting and Analytics Tools
To get some business insights out of master data, you should consider solutions from Tableau, Power BI, and Looker. Which one is better for your case? It depends on your business needs, however, smooth integration with MDM systems with real-time reporting is important for everyone. Custom report generation and data visualization features are nice to have if you want to see relationships and trends in master data more clearly.
9. Workflow and Automation Tools
To automate critical processes like data validation and approval workflows, there are highly effective automation tools from ServiceNow and Alteryx. While choosing a specific one, it makes sense to pay attention to customizable workflow features with business-specific approval processes, as well as automated updates on master data. It will be also nice to have alert and notification features for validation of errors and pending approvals.
10. Cloud and On-premise Infrastructure
As we mentioned before, for the best budgeting and security, it makes sense to consider both cloud and on-premise infrastructures. These solutions are available from AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, fully supporting flexible and scalable MDM implementations. Since the costs are so important here, probably the main thing you should consider is the transparent pricing of the vendor on the features you will require.
11. AI and Machine Learning Tools
The usage of AI and machine learning tools for data matching, cleansing, and anomaly detection is becoming increasingly popular in MDM. Solutions from Reltio and Tamr are the perfect example of this, as they offer high accuracy in key features. While selecting the most suitable solution, make sure that the option offers deep customization of AI models to fit the unique data characteristics of your organization, as well as explainability in the outputs.
Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“Here, at SPD Technology, we have extensive experience in implementing AI/ML solutions of any complexity, and MDM software is not an exception. In one of our recent projects, we leveraged predictive analytics to resolve critical data anomalies, lowering data inconsistency that harmed the decision-making process for our client. Our custom solution has proven to be far superior to existing alternatives on the market.”
12. API and Microservices Architecture
Having API and microservices architecture enables major flexibility in any MDM implementations, allowing each data function to operate as an independent service. Having API gateways like Kong or Apigee in your setup will ensure manageable and secure interaction between services. Microservice architecture also allows having a robust API version and deploying updates with minimal to no disruptions.
Challenges in MDM Implementation and Approaches to Their Mitigation
Developing a master data management strategy is a complex process, and the necessary infrastructure for its successful implementation is even more sophisticated. For this reason, some of the challenges are impossible to avoid completely, let’s analyze the most common ones.
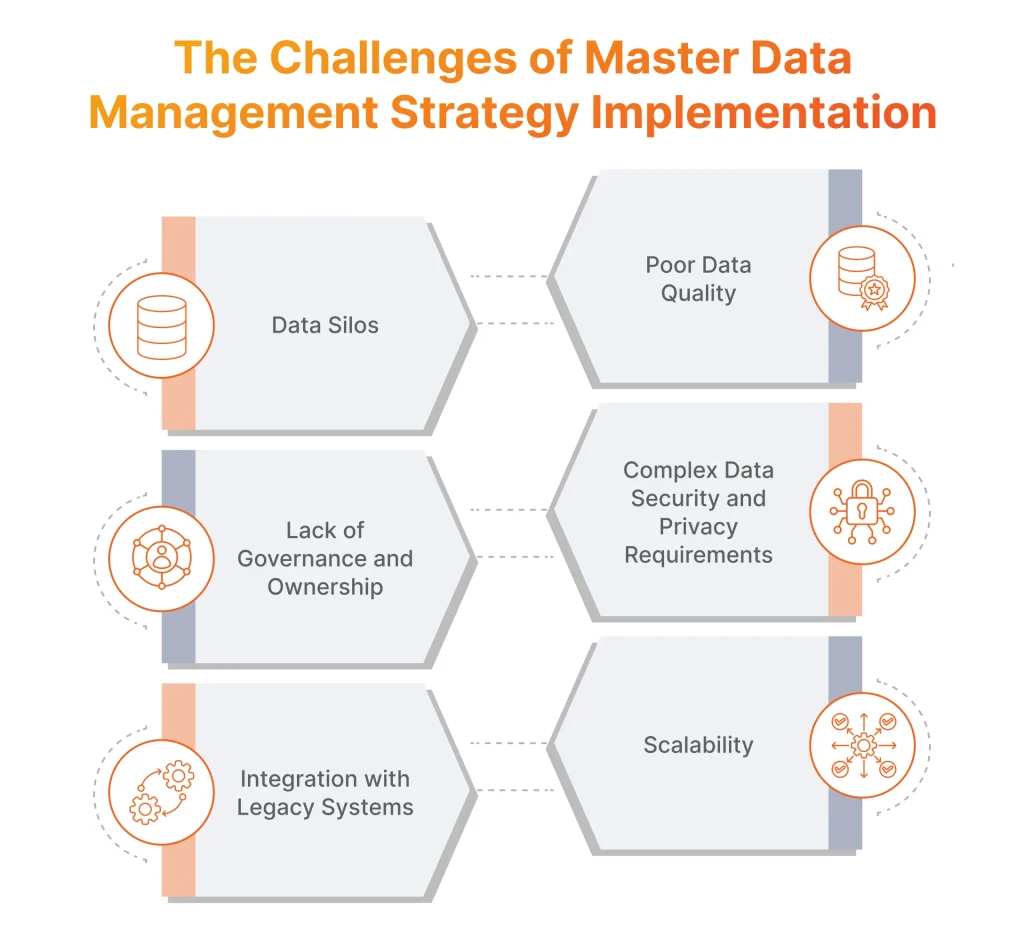
1. Data Silos
As the majority of companies typically store data across entirely different systems of different generations, data silos are a common problem that leads to a fragmented view of information. Here at SPD Technology, we overcome this challenge by:
- Consolidating information from all sources into a cohesive platform.
- Creating seamless data flow thanks to APIs, ETL processes, and middleware.
- Implementing streaming data processing for real-time data consistency.
2. Poor Data Quality
Duplication and inconsistencies harm data quality and reliability, making MDM programs for our clients less effective than they should be in terms of overall performance. We address this by implementing proven data quality management practices, including:
- Deploying automated tools for data cleansing, deduplication, validation, and enrichment.
- Providing real-time monitoring to continuously validate data against accuracy and completeness benchmarks.
3. Lack of Governance and Ownership
The absence of clear governance and ownership can put even the best master data management process strategy to a screeching halt. Time and time again, we dealt with these challenges by:
- Designing a comprehensive data governance framework that defines clear responsibilities for all parties.
- Leveraging governance tools to enable auditing, workflow approval, and policy enforcement.
4. Complex Data Security and Privacy Requirements
Maintaining data security and privacy is at the forefront of every MDM strategy. We bring deep, cross-industrial experience in this area by:
- Implementing custom encryption, strict access controls, and auditing features.
- Integrating privacy-by-design methods
- Incorporating data anonymization techniques.
5. Integration with Legacy Systems
Integrating modern master data management tools with legacy systems poses a unique challenge, as older systems lack the necessary compatibility with new tools. SPD Technology delivers custom solutions to deal with this problem, including:
- Developing custom connectors and middleware.
- Offering modernization roadmaps.
- Advising clients on phased approaches to avoid any business disruptions.
6. Scalability
With the growing data volume of data and increasing business impact of Big Data, there comes a demand for scaling capabilities, which is critical for the long-term success of the MDM. We secure the required scalability by:
- Designing MDM infrastructures with cloud and hybrid architectures.
- Implementing performance optimization techniques.
Why Choose SPD Technology for Data Quality Management Solutions?
We have proven experience in delivering global projects, closely following the latest innovations and constantly improving our approaches in developing MDM software solutions.
Expertise in Complex Data Environments
We handle master data aspects for projects across entirely different domains, sources, and systems. Our involvement is especially valuable in industries including Fintech, Retail, and Healthcare, which demand technical proficiency and strategic vision. With SPD Technology, you will get smooth data harmonization across all departments and critical business functions with consistent data flows.
Tailored MDM Solutions
We analyze the specific data management needs of each client, aligning our MDM solutions with particular business goals and visions. Our experts excel at coming up with tailored master data management strategies, addressing unique data structures, and keeping industrial requirements in mind, while maintaining clean, accessible master data, optimized to support each operational objective of our clients.
Advanced Data Quality Management
We set the highest standards for maintaining data quality as our priority, as the lack of attention to it leads to costly errors, inefficiencies, and unacceptable regulatory risks. Our teams leverage cutting-edge tools and methodologies to conduct rigorous management of data quality. We always ensure that only accurate data enters the systems of our clients, driving game-changing business insights.
Collaborative Approach
We are well-known for setting up close collaboration between business leaders, IT teams, and data stewards to align goals and ensure smooth implementation of the MDM strategy. In addition to structured communication, our company conducts workshops and provides a detailed master data management strategy document to keep stakeholders informed on every phase of the process.
Proven Experience in Data-Driven Industries
We know how to build software for highly regulated, data-intensive industries, as our experts have deep practical insights into the most complex regulatory requirements and operational demands. Here at SPD Technology, we learned to anticipate industry-specific challenges of our projects and are ready to view technical and business requirements in a comprehensive manner, proactively suggesting improvements for master data solutions.
Conclusion
The master data management global market is forecasted to reach $32.46 billion in 2028, compared to $15.34 billion in 2023, if Research and Markets is to be believed. There is no surprise in these impressive numbers and the fact that the market will double in the next four years, as more and more organizations see the business benefits of an MDM strategy. When done right, this strategy ensures consistent, centralized, and reliable master data across the entire organization, resulting in more informed decisions and streamlined operations.
Of course, there are some significant challenges involved, like managing data silos or maintaining high-quality data, ensuring its security at the same time. Solving these challenges requires a structured approach of vetted professionals, and we are here to help you with our data management services, taking on every aspect of the process and operating with the latest MDM strategy tools. We will turn your data into a winning asset, securing sustainable growth and driving innovation in your organization. Contact us to explore how we can help you, schedule a consultation, and get your MDM strategy example!
FAQ
What is Master Data Management Strategy?
It is a structured document that defines how a company manages core assets like customer, product, or vendor information. An effective MDM strategy ensures the reliability, accuracy, and consistency of data across the entire organization, establishing processes, tools, and policies to create a unified and trusted view of critical information.
Who Should be Involved in Master Data Management Strategy?
There are several key roles that should be collaborating during this process, including:
- Data Governance Team
- IT and Data Management Teams
- Business Units Representatives
- Data Stewards and Data Owners
- Compliance and Security Officers
