Having to collect and store data on a daily basis, organizations look for measures to extract the most value out of it. The best way to do it is to analyze this data, get meaningful insights from it and establish data-driven decision-making. Many companies agree that this approach to data can enhance operational efficiency, reduce administrative costs, and improve risk management.
According to Statista, a 2023 global survey showed that over 75% of businesses treat data as a catalyst for innovation and tend to use it effectively. To become one of such companies and stimulate data-powered innovation, it is important to design a data strategy roadmap. As a first step toward structured data management, we recommend navigating the structure and approach for establishing a data strategy roadmap, and this article will help you with this task.
Data Strategy Roadmap vs Framework
When it comes to data strategy, there are two terms that often cause confusion: data strategy framework and data strategy roadmap. It is totally understandable why people mix those two up as they are closely related. However, these terms serve different purposes in guiding data-related initiatives. Let’s figure out the difference between them.
The data strategy framework is the document that serves as a blueprint for data management, usage, and governance. It explains the main principles of the data strategy in theory as well as outlines its objectives and guidelines for how data will be handled across departments. In such a way, the framework offers a structure for achieving business goals connected to data.
The key components of the framework are:
- Data governance and quality management;
- Data security and privacy regulations;
- Analytics and data-driven decision-making;
- Technology infrastructure and tools;
- Skills and competencies.
On the other hand, the data strategy roadmap is a breakdown of the strategy. It illustrates how to implement the principles defined in the framework. The roadmap works on a more practical level and typically includes:
- Timelines for key data projects;
- Resources required for each phase (budget, tools, people);
- Prioritization of tasks based on business value;
- Metrics for tracking progress and success;
- Risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
As you might have guessed, the one does not exist without the other. The framework sets the vision and target results, while the roadmap splits them into actionable steps. A well-aligned framework ensures that the roadmap prioritizes activities that will bring the most value to the business. If the former clearly aligns with specific business objectives, then the roadmap has the potential to drive progress.
Looking to delve deeper into the data strategy framework?
We’ve got a dedicated article defining and explaining this concept!
The Importance of Building a Data Strategy Roadmap
Developing the data strategy roadmap may seem like a task that addresses the obvious. However, if you ever run a data project, you know how daunting it is to maintain focus and project course during implementation. Let’s consider the risk of neglecting the development of the roadmap and the benefits of having it.
Risks of Not Having a Roadmap
Without a coherent roadmap, you may encounter the risks of misaligning your initial project vision with the end results. That is why considering the following risks associated with the absence of the roadmap is crucial.
- Lack of Alignment: Teams may work in silos and move toward different goals that will result in wasted time and resources.
- Inefficient Resource Utilization: Without a specific project plan, the people, equipment, and technology allocated can cause unnecessary expenses.
- Compliance Issues: Due to neglecting some initiatives, it can become difficult to track compliance with regulation and, therefore, the risk of fines and penalties increases.
- Missed Opportunities: Important data initiatives can be neglected, which would keep the company from taking advantage of data-driven insights.
- Inconsistent Progress: It may be challenging to monitor progress or make required changes throughout project execution if there are no milestones in place.
Benefits of Implementing a Roadmap
Once an organization decides to equip your data endeavors with a coherent and relevant roadmap, it becomes easier to avoid the risks mentioned above and receive benefits, such as:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The roadmap helps to establish an approach to navigating data in real-time to help companies make relevant decisions.
- Cost Optimization: With initiatives clearly stated in the roadmap, the process of fund, infrastructure, and talent allocation becomes targeted and transparent.
- Enhanced Productivity: The roadmap highlights the bottlenecks in data workflows allowing companies to eliminate them and set up more streamlined processes.
- Improved Collaboration: The roadmap aids in bringing disparate teams and departments together around a shared data vision.
Key Elements of a Data Strategy Roadmap
Once you have established your data strategy and framework, you have the goals, objectives, and methods needed to achieve them. As the next step, you need to develop a roadmap to realize both the strategy and the framework. To craft the roadmap, you need to address crucial components.

1. Vision and Objectives
The vision shows the path towards long-term goals the company wants to achieve for its data. In this section of the roadmap, it is necessary to outline how exactly the organization’s stakeholders see the data strategy roadmap.
To better understand what initiatives will bring more value in working with data, you need to clear out what is the long-term vision for leveraging it. Think about how you expect data to enhance decision-making and promote data-driven culture: is your primary goal improved data quality or better customer insights, or other data-related needs.

Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“This step may be sometimes underestimated. However, our experience shows that defining the vision and breaking it into objectives helps to elaborate a more detailed approach to data and focus on what is really important.”
2. Assessment of Current Data Landscape
To grasp the full potential of the data, it is crucial to conduct an all-encompassing audit first. It gives clarity about current data sources, quality, and management practices.
Therefore, you need to understand where data is coming from (internal systems, external vendors, etc.), are there issues with accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of the data, and how well is data being governed, secured, and stored. This assessment provides a baseline, helping to identify gaps that need to be addressed in the roadmap.
3. Prioritization of Data Initiatives
Not all data initiatives must be pursued simultaneously, as it is impossible to do everything at once. However, you can emphasize one endeavor at a time and confidently move toward it. To understand what initiatives should go first, second, and so on, it is important to pay attention to their impact on business, efforts required to apply, and resources necessary to allocate.
- Impact: Addressing data activities with the highest impact first guarantees better returns, including more practical decisions, boosted earnings, and heightened operational efficiency.
- Effort: Focusing on allocating enough talent to specific data activities ensures elimination of miscommitment, early success and reduced risks among other reasons.
- Resources: Feasibility, cost-efficiency, and coherent risk management become possible once there are no talent, budget, or technical limitations.
Having these three factors balanced ensures that the roadmap is realistic and targets tangible results.
4. Resource Allocation and Budgeting
The budget, personnel, and technology must be specified and managed correctly for successful implementation of each data initiative. A targeted resource allocation reduces the risk of shortages, enhances team capabilities, and contributes to achieving project goals. You need to allocate:
- Budget: Correct financing supports data activities with the right tools and technology, access to expertise, and expenses for data storage and maintenance.
- Staff: Address skills gaps with training and additional hiring enhances chances of successful data projects delivery and ensures adapting to evolving technical requirements.
- Technology: Selecting the appropriate technology stack with tools supporting the project’s goals guarantees seamless integration with existing systems and scaling required when the organizational data needs grow.
To achieve a balanced budget, staff, and technology allocation in the roadmap, it is crucial to conduct needs assessment and consider overarching data objectives. These factors allow the company to stay focused on what’s important for the success of the project. Additionally, regularly reviewing these allocations with monitoring tools and performance metrics enables revisiting allocations to adapt to changing priorities or resolving unforeseen challenges.
5. Timelines and Milestones
Establishing key milestones makes sure that the project has a clear, measurable target, while a bottom-up approach to data initiatives guarantees that the project focuses on practical goals and is feasible. Paying attention to these two guarantees the data activities are executed within scope.
Phased implementation is another important factor to consider at this stage. It is desirable to break ambitious projects into smaller, manageable targeted milestones. Since data projects usually follow an iterative development model, this can make it challenging to set fixed timelines and milestones, as refinement and continuous improvement are common. As such, milestones may need to be flexible and adaptive to new findings or business needs.
6. Risk Management and Mitigation
Compared to smaller, more targeted data projects, creating a data roadmap is a complicated, diverse process that has more risks. For this reason, planning risk mitigation measures should be taken into account from the very beginning. In such a way, it becomes possible to keep initiatives within scope, prevent unnecessary financial and operational setbacks, and safeguards the organization’s data assets. Some of the risks may be:
- Budget Overruns: Data initiatives need costly technology investments, specialized tools, and external expertise. Without detailed financial planning and regular budget revisions, costs can get out of control.
- Lack of Necessary Skills: Working with data requires skills in data science, analytics, engineering, and governance. Lack of skill assessment, specialized training, and hiring additional experts can result in failure in achieving data goals. .
- Technology Challenges: Integrating new technologies, ensuring data security, and maintaining compatibility with legacy systems create technical obstacles. To overcome them, it is essential to pilot test technologies as well as choose adaptable tools.
Preparing fallback plans for high-risk scenarios will help minimize disruptions and maintain progress.
How to Create a Data Strategy Roadmap
The creation of the roadmap requires following several crucial steps. While some of the steps might require modification as the company will acquire new findings along the way, the steps mentioned below serve as a solid guide for establishing a coherent and relevant to company’s goals roadmap.
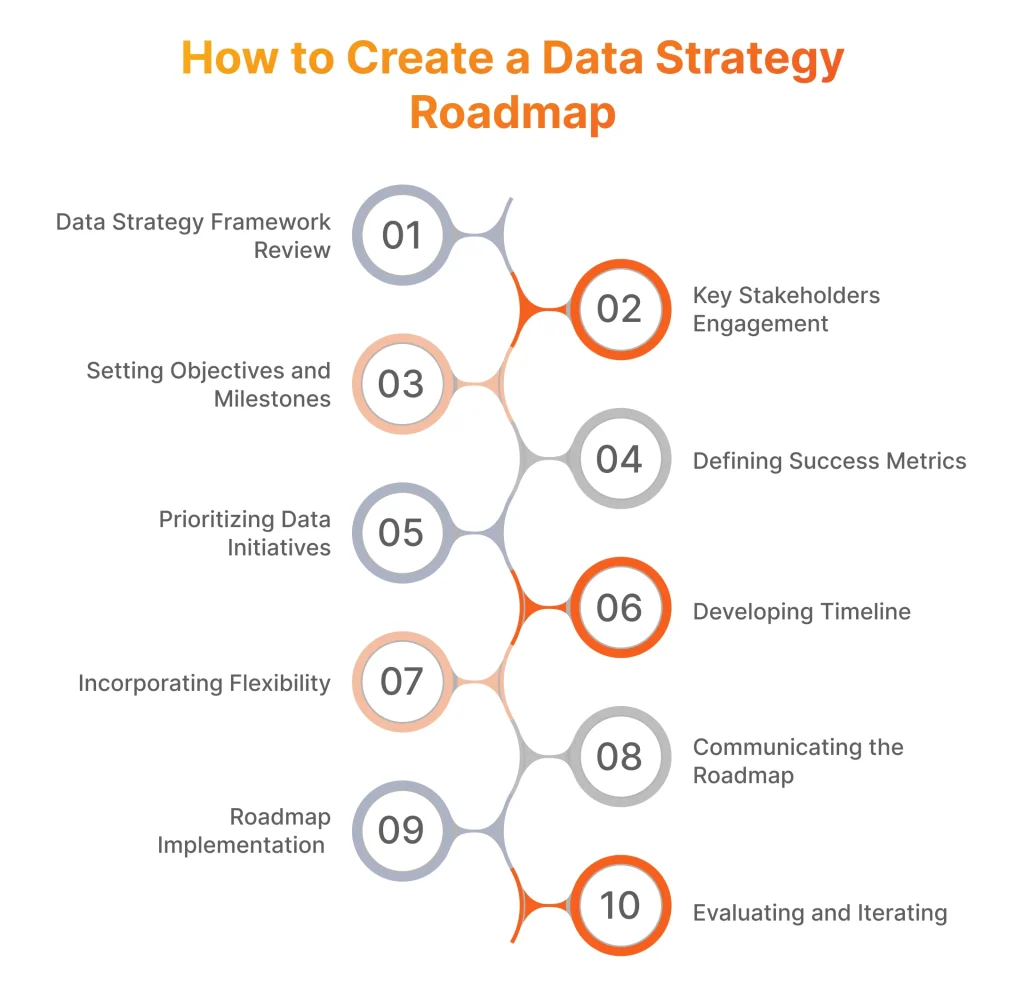
Step 1: Reviewing and Understanding the Data Strategy Framework
The framework establishes the strategy’s core principles. For this reason, before developing the roadmap, it is essential to review the data strategy’s content and, in particular, the data framework. Focusing on the core components of the framework allows shaping a coherent approach for executing data initiatives. Those components are data governance, quality, integration, security, and analytics. Having all of them cleared promotes forming a holistic view of the project undertakings as well as possible risks and opportunities connected to technical capabilities, resource allocation, etc.
Step 2: Engaging Key Stakeholders
The roadmap needs to be crafted considering the expertise from different departments. This ensures better overall alignment with the overarching business strategy. To achieve that, it is vital to invite stakeholders from IT, marketing, operations, leadership, and finance to contribute to the roadmap development. Stakeholder mapping, collaborative workshops, and regular meetings can help include different expertise and viewpoints. With such a contribution, the roadmap becomes a detailed guide for the effective execution of data projects.
Step 3: Setting Clear Objectives and Milestones
Outlining goals and milestones comes next as they help understand how to build the project according to the principles set in the framework. Goals may be improving the quality of data, ensuring the data is accessible across departments, and preparing data for analytics purposes. The examples of milestones can be the implementation of data governance policies or the deployment of a centralized data platform. To track progress and make sure your teams remain on the same page, it is vital to break down the major goal (or a few of them) into precise milestones.
Step 4: Defining Success Metrics
In order to see whether the data initiatives bring results, setting clear KPIs emerges as a crucial step. They assist in assessing performance and making the right adjustments as the project progresses and optimizing results. KPIs can be used to measure the success of system integration by reducing data silos, track advances in data quality through accuracy scores, or track the adoption of analytics by calculating the percentage of decisions made based on data.
Step 5: Outlining and Prioritizing Initiatives
After data initiatives receive clear KPIs, they need to be ranked in the order of importance. Implementing data governance policies can be number one priority, or this place can be taken by such activities as improving data accuracy and consistency, consolidating data from several sources, and transitioning to a cloud-based platform. Such a prioritization necessitates assessing elements such as cost, viability. Once these factors are aligned with strategy goals. The company can expect correct resource allocation and, later, greater ROI.
Step 6: Developing Timeline
A realistic timeline is key to smoothly rolling out an enterprise data strategy roadmap. It should outline concrete tasks, like setting up data governance, upgrading infrastructure, or developing analytics models. Each task needs precise responsibilities, with specific professionals assigned to each of them, making sure that everyone contributes and stays on the same page. Plus, setting firm deadlines is essential to keep the project moving forward and on schedule.

Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“A roadmap can be a living document where timelines, responsibilities and deadlines are adjusted as needed to reflect changing priorities or unexpected challenges.”
Step 7: Incorporating Flexibility
It’s essential to have a flexible roadmap because technology evolves quickly, and data needs changes as the project continues to unfold. To keep up with these changes, the roadmap should include strategies for adopting new tools, adjusting to the company’s growing needs, and staying ahead of emerging trends. It’s essential to be ready to tweak the roadmap along the way without slowing things down. This ensures it remains relevant and effective over time.
Step 8: Communicating the Roadmap
Timely resource allocation and cross-departmental project alignment are essential for a well-coordinated strategy implementation. This ensures that everyone involved is aware of the roadmap’s objectives, milestones, and KPIs. Proper resource allocation guarantees that teams have the necessary tools, skills, and budget to execute their tasks, while open communication and regular meetings promote cooperation and support across the company.
Step 9: Implementing the Roadmap
Project management tools, which guide the project in alignment with Agile principles, facilitate the work with the roadmap and make sure that teams complete their assignments on schedule. Agile methodologies such as Scrum and Kanban emphasize iterative development, continuous feedback, and cross-functional collaboration. With their help, teams remain adaptable and respond to changes or challenges swiftly. Methodologies also promote scheduling frequent check-ins for monitoring development and addressing problems.
Step 10: Evaluating and Iterating
After implementation of the data strategy roadmap, the process of evaluation and optimization comes up as the next integral part of an organization’s data maturity. Evaluation helps assess whether data initiatives are meeting KPIs, while optimization allows for fine-tuning processes. This can be achieved through regular performance reviews, feedback loops, and leveraging analytics to identify areas for improvement. Thanks to continuous evaluation, the data strategy remains agile and brings results over time.
Data Strategy Roadmap Template
In order to give you a clear picture of what the roadmap is, we offer you to check one of the possible data strategy roadmap examples.
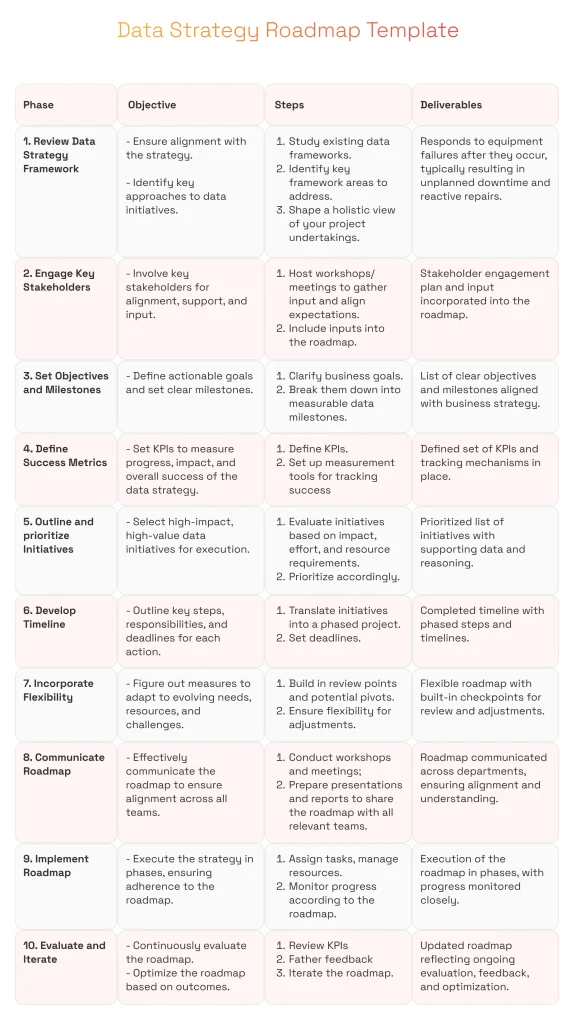
This is one of the many data roadmap examples, and its phases are adaptable to specific data project requirements. However, this general structure introduces the core steps required for a detailed data roadmap.
Data Strategy Roadmap Development: Core Challenges
While working on numerous roadmap developments and implementations, we experienced several roadblocks that can hinder the process. Below we share the most common complexities we encountered and uncover how we approach their resolution.
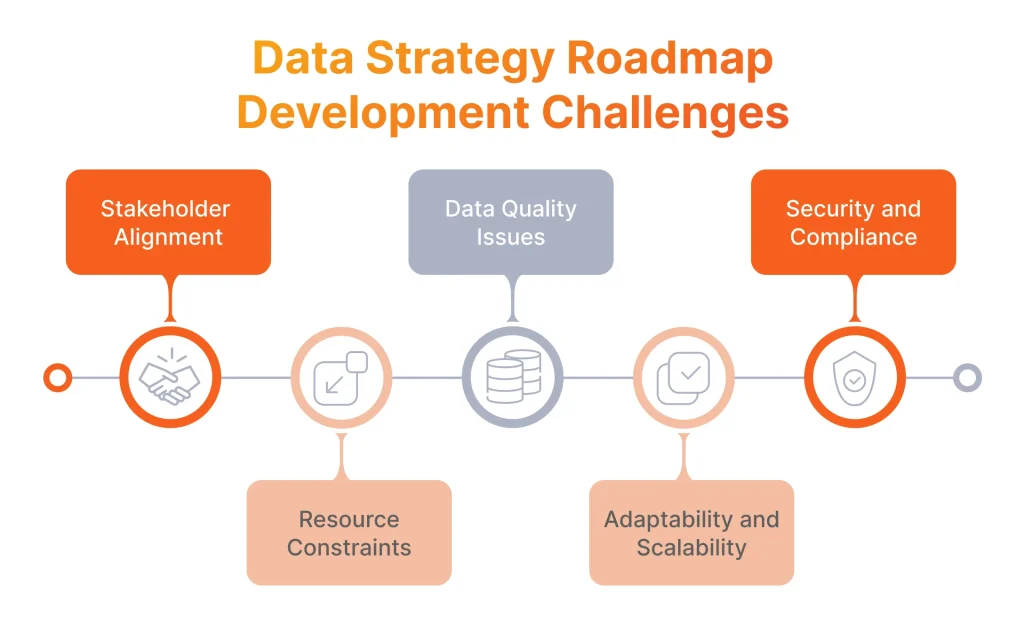
Stakeholder Alignment
Stakeholders in an organization often come from various departments, such as IT, marketing, finance, operations, and senior leadership. While working on the roadmap, we need to align stakeholders’ perspectives, priorities, and objectives. Otherwise, misalignment among them could cause conflicting objectives, which, in turn, would lead to failed goals.
At the same time, when different stakeholders have conflicting goals, it usually takes a longer time to reach an agreement. As a result, decision-making slows down and the project completion is postponed. Our team elaborated several tactics to avoid this bottleneck.
- Structured Communication: Regular workshops, meetings, and collaborative sessions help focus on aligning business objectives with data initiatives.
- Clear Value Proposition: Highlighting the business value of each data initiative to different stakeholders shows how data solutions can directly impact their specific goals.
- Steering Committee: Establishing a steering committee composed of key stakeholders from different departments enables consistent communication and shared ownership.
Resource Constraints
When building data strategy roadmaps for clients, we face resource constraints, such as limited budgets, a lack of available talent, or competing priorities. These constraints are the reasons why building the necessary infrastructure for data initiatives and acquiring data science expertise become burdens.
In such a way, expenses for technology platforms, hardware, cloud services, software tools, and advanced analytics solutions are hard to manage. The same applies to personnel, such as data engineers, data scientists, and analysts. To navigate these challenges, we usually:
- Prioritize High-Impact Initiatives: Building a hierarchy of initiatives in accordance with potential ROI allows focusing on the data initiatives with the best potential value.
- Apply Phased Approach: Smaller, manageable phases can be funded incrementally. As a result, the companies achieve steady progress.
- Leverage External Expertise: Expertise can be accessed and full-time staffing expenses can be avoided by outsourcing some tasks or collaborating with outside data specialists.
- Choose CaaS Models: SaaS models and cloud solutions provide scalability without requiring significant upfront infrastructure funding.
Data Quality Issues
Accenture states that 88% of companies find it hard to translate data into meaningful insights for the business. From our experience, this happens due to incomplete, inconsistent, or inaccurate data that significantly slows down the progress.
When we have to deal with poor-quality data, our team must spend extra time cleaning, verifying, and organizing the data before we can use it effectively. This not only delays the execution of data initiatives but also diverts valuable resources and attention away from higher-priority tasks. To prevent such issues, our team engages in:
- Regular Data Audits: Implementing regular data audits helps identify inconsistencies and gaps early on and address them before they affect the overall data processes.
- Automated Data Cleaning: Utilizing automated data cleaning tools assists in streamlining the identification and resolution of errors, and, as a result, reduces manual intervention.
- Establish Data Quality Management Frameworks: Implementing a continuous data quality management process sets clear guidelines on how data should be collected, processed, and stored.
Adaptability and Scalability
As the businesses grow and the market requires more, our clients often ask us to help them handle increasing volumes of data. Additionally, we are often set with the task to leverage more sophisticated data-driven insights since the businesses want to overcome competition.
Such a dependance on data causes bottlenecks for companies that use outdated data infrastructures, meaning they cannot scale and adapt to advanced technologies. For instance, on-premise servers or outdated databases can not accommodate the need for flexibility and greater storage capacity to manage larger volumes of data. To manage these complexities, we offer to use:
- Modular Infrastructure: Building the data infrastructure using a modular approach allows for easy upgrades and integrations as new technologies or requirements appear.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Opting for cloud solutions brings scalability and the ability to manage large data volumes based on the company’s needs.
- Future-Proof Technology Stack: Choosing technologies and platforms built to evolve makes sure that the preferred data infrastructure can easily adapt to future needs.
Security and Compliance
We often have to deal with changing data requirements as the data usage, in turn, needs to be complied with regulations that are frequently updated. Staying compliant requires businesses to continually monitor legal updates and adjust their data handling policies. When dealing with companies operating across multiple regions, we face even greater complexity, as our clients must ensure compliance with different regulations simultaneously.
Another thing imposed not only by regulations but also by the desire to keep a trustworthy brand image is security measures. Companies must protect personal information from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches. To avoid penalties for neglecting security and compliance, our team suggest to:
- Establish a Clear Security and Compliance Framework: This helps define protocols for data protection, breach response, and user access control.
- Use Automated Compliance Tools: In such a way, it is possible to monitor regulatory compliance and notify teams in case of changes.
- Establish Data Encryption and Access Control: This brings the possibility to keep unauthorized users away from sensitive data.
Develop Data Strategy Roadmap: Professional Approach
For every company seeking to use data as a strategic asset, creating a data strategy roadmap is an important but difficult task. While some companies may attempt to develop a data strategy internally, asking for professional assistance can provide more industry-related and technical expertise to the table.
With a plethora of expertise dealing with many industries such as FinTech, Healthcare, Legal, eCommerce, and data management, SPD Technology offers a variety of knowledge to the table. Our data architects and business analysts can create a coherent roadmap and tailor it to your specific goals by using our knowledge of emerging trends, best practices and by calculating in advance possible hidden challenges. Partnering with us, you can rely on:
- Tailored Solutions to Fit Unique Business Needs: We prioritize a tailored approach and are ready to come up with a customized solution to take into consideration every nuance of your business.
- Proven Expertise in Data Management: With over 18 years of experience, we gained valuable expertise in data science and are ready to offer you access to best practices and cutting-edge methodologies to ensure your data strategy roadmap is both innovative and effective.
- Holistic and Practical Approach: Thanks to numerous projects we delivered data expertise for, our team knows how to develop data roadmaps that will be actionable and aligned with real-world business operations.
- Risk Mitigation and Compliance: We ensured compliance with GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and other regulatory requirements. SPD Technology focuses on risk management for you to confidently pursue your data endeavors knowing that you are operating within all legal frameworks and industry standards.
- Focus on ROI: Data strategies can be resource-intensive, but our approach ensures that every dollar invested yields significant returns. With a clear focus on ROI, we help you realize value from your data sooner and more effectively.
Robust Data Strategy for BlackHawk Network: From Vision to Execution
Our client, BHN, approached us with the challenge of consolidating data from eight eCommerce platforms. The complexity of the task left the client uncertain about where to begin. We were tasked with developing an enterprise data strategy for integrating the disparate software components of these acquired platforms into a unified system capable of supporting key functions like onboarding, accounting, finance, fraud detection, and risk management.
The strategy was focused on a range of data-related tasks. To meet the project goals, we planned data migration and reconciliation, utilizing modern tools to securely transfer data of any complexity while ensuring its integrity. This was critical for a company handling $30 billion in annual load value.
The strategy also included the work on five ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) microservices to extract data from the client’s systems, including legacy platforms, and transform it to align with the new domain model. Plus, we identified the need to build four microservices for monitoring changes and updating data across all ecosystems in real-time.
After the client examined our strategy, BHN asked our data engineering team to help the company put it into action. By creating a consolidated system architecture, we enabled cost savings for BHN, streamlining processes, reducing redundancy, and eliminating the need for extra resources. The consolidation resulted in $200,000 per month in operational savings by replacing legacy systems, significantly lowering server, database, and technical support costs.
Conclusion
The data strategy roadmap serves as a strategic tool for delivering data projects. It drives the progress thanks to stating core elements of data initiatives, such as vision, goals, existing data evaluation, and prioritization of data activities. To ensure smooth execution of data projects, the roadmap also outlines resources and budget, timelines and milestones, and risk management measures.
In case companies neglect elaborating an enterprise data strategy roadmap, several risks emerge. Those are resource misallocation, revenue loss, low-quality data, poor data management, vulnerabilities in security measures. Nonetheless, once equipped with the roadmap, businesses can gain from streamlined funding, smooth integrations, data-driven decision-making, scalability, and innovation opportunities.
There are ten steps necessary to complete to design the data roadmap. Reviewing the data strategy framework comes first, followed by collaborating with stakeholders, outlining goals and defining success criteria. After, companies must prioritize data activities, set timelines and deadlines, take care of the roadmap flexibility, and, finally, implement it. Monitoring of the progress comes last, yet remains crucial for adapting the roadmap to evolving business needs.
The task of creating the roadmap might seem complex. There are some challenges that may hinder the development and implementation of the roadmap, namely stakeholder misalignment, resource constraints, data quality, adaptability, and security. However, with a professional and detailed approach, it is achievable. We know this because we have created and implemented data strategies, including roadmaps, for many clients. If you need a consultation, feel free to contact us.
FAQ
What Is a Data Strategy Roadmap?
A data strategy roadmap is a structured plan outlining how an organization will manage, use, and leverage data to achieve its business objectives. While developing it, data strategy consultants and data analysts include goals, key initiatives, timelines, and resources needed to ensure data supports strategic decision-making and operational efficiency.
How to Create a Data Strategy Roadmap?
To create a data analytics strategy roadmap, start by defining the company’s objectives and needs for utilizing data. Assess current data capabilities, identify gaps, and set clear goals. Develop a plan outlining key undertakings, timelines, and resource allocations. Regularly review and adjust the roadmap to align with evolving business needs and technologies.
How Do You Identify the Key Initiatives in a Data Strategy Roadmap?
You can define key actions in a data platform roadmap by analyzing business goals, data needs, and current capabilities. Engage relevant stakeholders to understand their requirements, and prioritize initiatives based on impact and feasibility. Ensure that each initiative aligns with strategic objectives and addresses gaps in data management and usage to drive value.


