With digitalization accelerating across industries, data production has skyrocketed. Organizations now generate an astounding 328.77 million terabytes of data every day, if What’s The Big Data Report is to be believed. However, the accumulation of data alone does not ensure success, as specific approaches are required to get value from it.
Forbes, in turn, states that data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to acquire customers, 6 times as likely to retain them, and 19 times more likely to become profitable, while Deloitte reports that among 29 Chief Data Officers, 61% named delivering on data strategy as a top 3 priority.
So, there is a critical importance of having a structured approach to managing and leveraging data. A data strategy framework serves this goal, allowing for improved decision-making, boosting operation efficiency, and enhancing customer insights, as well as prioritizing data quality and governance.
What Is a Data Strategy Framework?
This is a structured set of guidelines or principles developed through a data strategy development process, outlining the processes, tools, technologies, and governance structures required to manage data effectively across an entire organization. It provides the foundation for understanding and organizing complex systems and processes, serving as a skeleton that outlines key components and their relationships.
Data Strategy Framework is the first step for effective data management strategy, ensuring that data is collected, stored, processed, and analyzed in close alignment with the organization’s strategic goals while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
Key components of the data strategy framework typically include:
- Data Governance sets policies, standards, and roles for managing data assets.
- Data Architecture defines the overall structure of data storage, integration, and flow within the organization.
- Data Management encompasses best practices for data collection, quality control, lifecycle management, and master data management.
- Data Analytics is all about leveraging data for insights and utilizing tools like Business Intelligence (BI) platforms to support data-driven decision-making.
- Data Security and Compliance ensure the protection of data through robust security measures and adherence to relevant legal and regulatory requirements.
- Data Culture and Literacy promote a data-driven mindset across the organization and integrate data into everyday decision-making processes.
A Data Strategy Framework is closely aligned with the business goals and IT infrastructure of an organization. It focuses on specific goals, like boosting revenue or performance improvement by suggesting solutions according to Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics. Ultimately, the framework ensures that the organization’s IT infrastructure is using the right data storage solutions, integrating data across various systems, and making the IT environment scalable and secure.

Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“In our projects, we always provide a clear data strategy roadmap, data maturity assessment, data governance framework, and data-driven business transformation planning allowing our clients to know precisely what we are going to do in their unique scenario. We take care of high-level guidance and strategic planning, helping our clients to keep data initiatives and business goals in perfect synchronization.”
Why Your Business Needs a Data Strategy Framework
The truth is that having a comprehensive data strategy framework is becoming less of an option, and more of a key element for organizations to gain a competitive advantage and maximize the potential of existing information. Let’s discuss why it should be considered an important element of your overall business strategy.
The Risks of Not Having a Data Strategy

First and foremost, there are potential risks of not leveraging data strategies which include but aren’t limited to the following ones.
Data Silos
Data silos form when the information is scattered across different departments or systems without a comprehensive data strategy or clear logic. This fragmentation prevents business users from seeing the full picture, resulting in such blockers as inconsistent reporting, duplicated efforts, and missed insights. Data silos also make it very difficult to enforce consistent data governance and quality standards.

Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“Having nearly two decades of experience in Fintech, a quite common example of a data silo that we encountered countless times in our projects comes to mind. Imagine a financial services company that has different systems for managing client accounts, loan applications, and investment portfolios. Because each system operates independently of the other, there is minimal to no data sharing between them. So, when the customer applies for a loan, the processing team may spend a lot of time reviewing personal financial information from different sources and there will always be a risk of human error.”
Compliance Issues
Without leveraging data strategy consulting services and having an appropriate way to handle information, your business will always be in danger of not complying with regulatory requirements. Data protection laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA have strict guidelines on how data should be handled, stored, and shared. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, legal actions, and reputational damage, which are especially damaging in industries like Healthcare and Finance that operate with highly sensitive data.
Missed Opportunities
Having a good data strategy allows businesses to truly be in charge of the information they have, as it contains game-changing insights on customer behavior and the dynamics of the business environment the company operates in. Without it, organizations may be missing out on major opportunities to grow and improve.
Benefits of Implementing a Data Strategy Framework
On the contrary, the companies that treat their information as a strategic asset get several competitive advantages.
Improved Decision-Making
The key personnel in your organization will have full data access and the ability to make decisions based on facts and relevant updates, rather than guesswork, proactively responding to any changes or emerging trends. Additionally, you will be able to synchronize all business units and have a holistic overview of all inputs, getting the fullest perspective possible.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Having data flows run seamlessly across the entire organization, you will be able to optimize and streamline key operations, for example, using integrated data to develop accurately targeted marketing offerings or reducing excess inventory by integrating sales and supply data. Regardless of the process being optimized under the umbrella of a unified data strategy framework, this approach improves operational efficiency by:
- Reducing duplication of actions
- Minimizing efforts
- Improving collaboration across all teams
- Open new opportunities for process automation.
Enhanced Customer Insights
Getting a deep understanding of your customers is the first step to offering personalized experiences that will lead to better profitability. With the data analytics strategy framework, your business can gain insights into customer preferences, recurring behaviors, and the most significant pain points. By harnessing the business impact of Big Data, you can transform these insights into actionable strategies that drive targeted marketing efforts, optimize product offerings, and enhance customer engagement.
Increased Agility and Innovation
By establishing a structured approach to data management, organizations can quickly adapt to changing market conditions and emerging trends. As a company that constantly pushes innovation forward, we acknowledge and have proven experience that creating a data strategy allows our clients to be much more agile and responsive to market changes compared to other organizations in the respective niches.
As a part of one of our recent projects, we helped a comprehensive platform tailored for heavy construction companies to develop a robust Data Analytics system, managing and analyzing an extensive dataset comprising 70+ million records. Our experts engineered a client-facing OLAP Data Lake system, specifically tailored to manage data operations in the construction domain, ensuring high performance and near real-time data availability.
Data-Driven Culture
Implementing a data strategy framework helps to develop a data-driven culture, where decisions are based on accurate, real-time insights, and not guesswork. This significant shift enhances profitability and operational efficiency as businesses become more flexible in responding to market trends and optimizing processes.
Foundation for Further Evolution of AI/ML
Finally, a well-structured data strategy framework serves as the base for future AI and machine learning initiatives. By having high-quality, organized data, businesses can integrate AI/ML technologies more easily, driving automation, extracting predictive insights, and enhancing decision-making. This preparation secures and accelerates business evolution, positioning organizations to capitalize on cutting-edge innovations, and surpassing competitors.
Real-World Examples of Companies That Benefited from a Robust Data Strategy
Some of the world’s leading companies are turning data strategy into a key business model, basing their core services on it. Let’s review the outcomes they get by approaching their data strategically.
Netflix
Thanks to user data analysis and an advanced ML-powered recommendation system, Netflix became a dominant player in the streaming market, ending up in 2023 with $33.7 billion in revenue according to Business of Apps. Tailored recommendations transformed into a prime feature of the platform, which became an industry standard for streaming services and attracted over 270 million active subscribers.
Amazon
In another prominent example, Amazon’s recommendation system has been the centerpiece of the platform for over 20 years and truly shows how data capabilities and Artificial Intelligence can elevate an eCommerce platform. Not only does it offer accurate recommendations, but also actively adjusts prices according to the demand and helps with inventory management.
Walmart
As for another global leader, Walmart’s data operations include using data analytics for supply chain optimization and inventory management. Their powerful algorithms analyze sales data, weather patterns, customer behavior as well as a variety of other factors to make the right supply chain adjustments and ultimately enhance overall operational efficiency.
Procter & Gamble
P&G has invested in data analytics to understand consumer behavior and improve product development. Specifically, they utilized data analytics during the launch of their Tide Pods, analyzing customer feedback and purchasing data from test markets, they identified consumer preferences for convenience in laundry products. This insight drove marketing strategies and led to a successful nationwide rollout.
Coca-Cola
This company is well-known for using data analytics to drive marketing strategies and product innovation. In particular, Coca-Cola’s Freestyle vending machines can track consumer choices and provide granular data about flavor preferences in different regions. This helped to launch some popular products, like Sprite Cherry.
Core Components of a Data Strategy Framework
Each component of the enterprise data strategy framework plays a critical role in ensuring that information is effectively managed, analyzed, and utilized across the organization.
Data Governance
Data governance rules are all about creating policies and responsibilities to ensure that data in the organization is handled properly.
Key Elements
- Policies and Standards: They define how data is accessed, shared, and retained, including data access policies, data sharing protocols, and data retention guidelines.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clear assignment of roles to manage data assets, including data stewards, custodians, and users.
- Decision-Making Framework: A structured process for approving data-related decisions, ensuring accountability and compliance.
Each of the data governance elements is directly influenced by regulatory compliance since all organizations must adhere to relevant laws like GDPR and CCPA, as well as follow the current standards for the respective industries. The internal structure and flows in the organization also influence heavily how data governance policies must be enforced.
Typically, to implement a data governance framework companies create a governance committee that works on the creation of the data governance policies and monitors their enforcement.
Data Architecture
Data architecture refers to the design and structure of an organization’s data environment.
Key Elements
- Data Storage Solutions: It should be determined where the data is stored, on-premises databases, cloud storage solutions, or hybrid environments.
- Data Integration: The information should be seamlessly integrated from various sources, delivering a unified view.
- Data Pipelines: These are workflows that ensure data flows efficiently across systems and ends up in the right department on time.
Among the key considerations that influence the decision on data architecture are implementation costs, performance, and scalability. For example, a leader of an organization might recognize the advantages of cloud storage like lower upfront expenses and impressive scalability, but still choose on-premise storage due to security concerns. Based on our experience, we recommend taking a deeper look at cloud computing infrastructure benefits to discover whether this approach fits your business needs.
Despite what storage you choose, it is essential to design scalable data pipelines while implementing data architecture. Once the architecture is set, organizations must continuously monitor data flow to detect possible bottlenecks and take action on further optimizations.
Data Management
It is the systematic process of collecting, storing, organizing, and maintaining data in a way that ensures the highest accessibility, accuracy, and security throughout its lifecycle.
Key Elements
- Data Collection: A set of practices that ensure data is gathered consistently.
- Data Quality Management: A process that ensures that data is accurate, complete, and reliable.
- Data Lifecycle Management: A defined way of managing data from its creation and usage to archival and eventual deletion.
The biggest influence on data management practices is probably the amount and the complexity of data that must be handled. With the increasing amount of information, companies should improve their storage standardization and lifecycle management.
Effective data management starts with setting up data collection practices, and ensuring that collected information is standardized and consistent. Maintaining high-quality information is critical here, as it directly impacts decisions that will be made according to it.
Managing the entire data lifecycle, from collection or creation and usage to archival in existing data infrastructure and deletion, is essential for optimizing storage costs, ensuring compliance, and preventing any possible data overload. If you need any help with it, we advise you to use our Data Management Services to do this process right.
For one of our B2B clients, we leveraged ML and OpenAI for automated data collection and processing. As a result, we achieved a 5x cost reduction on faster task completion and enhanced staff efficiency.
Data Analytics
It is all about using statistical and computational methods to extract meaningful insights from raw data.
Key Elements
- Analytics Types: There are three distinctive analytics types. Descriptive focuses on understanding past data, Predictive is forecasting future trends, and Prescriptive suggesting specific actions.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: Off-the-shelf products that visualize data and provide actionable insights.
The main factor in choosing data analytics strategies is the business goals of the company. For example, when the company is focusing on customer retention, it will make sense to implement predictive analytics, while when the analysis of previous performance is required, introducing descriptive analytics is a way to go. The availability and the quality of data also play a major role, as even with the most sophisticated analytics tools, the results will be limited without correct information.
To turn raw data into actionable insights, it is mandatory to have a strong analytics strategy, with appropriate analytics methodologies — descriptive, predictive, or prescriptive analytics, based on current business needs. Leveraging Business Intelligence (BI) tools such as Tableau, Power BI, or Qlik is also crucial, as they provide powerful visualization capabilities that make data accessible and comprehensible to decision-makers.
Data Security and Compliance
It involves protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and loss while ensuring that the organization adheres to all active regulatory standards and industry best practices.
Key Elements
- Security Measures: Specific techniques that focus on preventing any breaches or losses.
- Compliance: Ensuring data practices align with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
The changes in the regulatory environment are the main reason for adjustments in data security and compliance strategies. The choice of technological infrastructure can also affect how security protocols are designed and maintained.
To comply with the latest data security regulations, several techniques can be implemented, including data masking, anonymization, and encryption. Organizations should keep updated with the relevant regulations and ensure that their data practices meet current requirements, as the regulations are constantly changing.
Data Culture and Literacy
It refers to the adoption of data-driven thinking and decision-making in the organization, ensuring that all employees have the best knowledge of how to use data effectively.
Key Elements
- Training and Education: Introducing training programs that enhance data literacy.
- Leadership Advocacy: Promoting a data-driven culture by leadership.
- Data Accessibility: Ensuring that data is accessible and comprehensible to all departments.
Probably the biggest factor here is leadership support, as the key stakeholders must advocate for a data-driven culture, setting the tone for the rest of the organization. Furthermore, the user-friendly tools to achieve this goal must be easily accessible to every member of the organization. If you need any help with this task, contact us for data management consulting, and we will gladly share our expertise.
Organizations should be ready to invest in training programs and improve the data literacy of employees across all departments. Leaders should always reward and recognize data-driven initiatives among employees and make them an essential part of everyday activities in the company.
As you see, there are a lot of components to consider while building a data strategy framework. To navigate these complexities, we advise you to leverage strategic technology consulting and seek guidance from experienced Data Architects and other qualified experts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Developing a Data Strategy Framework
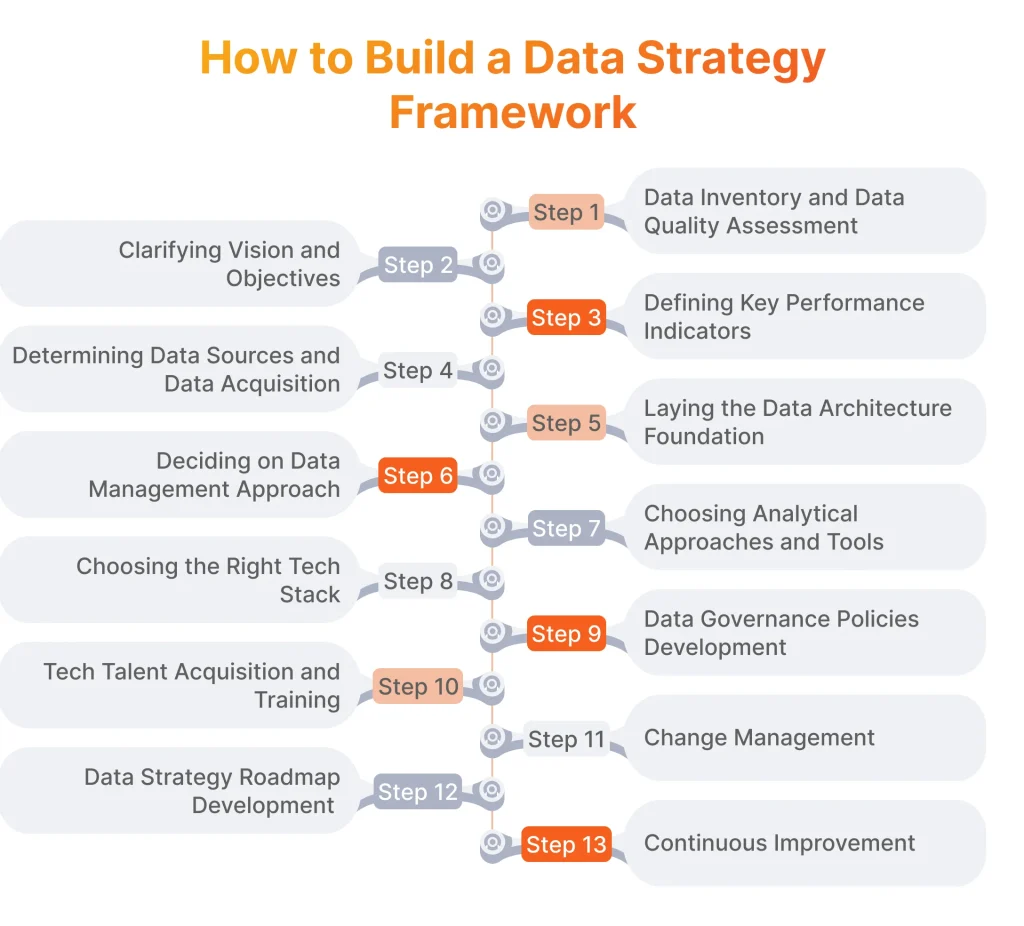
Now, let’s dive deep into how to build a data strategy and figure out how it’s done in the real world.
Step 1: Data Inventory and Data Quality Assessment
It all begins with understanding your current data management practices to identify strengths and weaknesses. Here is what to assess.
- Data Inventory: the process begins with an inventory of the organization’s data assets, including databases, spreadsheets, cloud storage, and any third-party data sources, documenting where the data resides, how it’s being used, and who has access to it.
- Data Quality Assessment: evaluating the quality of data by identifying inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and gaps.
- Data Management Practices: assessing the effectiveness of a company’s current practices, as well as data governance policies, data integration capabilities, and security measures.
- Technology Audit: examining the tools and technologies the business currently uses, and making sure they are up-to-date.
Step 2: Clarifying Vision and Objectives
It is important to sync with key stakeholders in understanding how leveraging data can ensure revenue growth and operational efficiency. Below are the steps to ensure a perfect alignment of a data strategy framework with the business goals:
- Identifying Business Objectives: First, it is necessary to define the key goals the business aims to achieve, for example, revenue growth, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction. It is also important to ensure that all of the identified objectives are SMART – specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Assessing What Data is Needed to Support These Business Objectives: The next sub-step is determining what types of data are essential for achieving each business objective. For example, if the business objective is to improve customer satisfaction (measured with Net Promoter Score (NPS), then the company will need transactional data on sales and order details, and operational data on customer feedback and support inquiries.
- Involving Key Stakeholders from Various Departments: This step involves engaging department heads and key stakeholders from marketing, sales, finance, and IT to gather holistic input and ensure their data needs are considered. The goal of collaborating with them is to align the data strategy with their respective departmental goals and KPIs.

Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Manager at SPD Technology
“At this stage, according to our experience, it is very important to obtain buy-in from the leadership. Explain the value of future changes, and highlight the direct impact on business metrics, to keep everyone engaged in the process and maximize the benefits.”
Step 3: Defining Key Performance Indicators
The next step is determining what success is in your businesses’ particular case and what specific outcomes the company aims to achieve. Some of the KPIs, depending on the business objectives, could be:
- Data accuracy rates
- Time spent on data preparation
- The number of data-driven decisions
- ROI from data initiatives.
When defining the KPIs, it is crucial to establish baseline metrics to compare against over time and leverage gained insights for the improvement of the data strategy.
Step 4: Determining Data Sources and Creating a Data Acquisition Plan
Next, the organization must determine all data sources it needs to rely on. Then, it is necessary to create a data acquisition plan that should clearly outline how this information will be collected, integrated, and made accessible to different departments.
Here are the key steps:
- Identifying Internal Data Sources: CRM systems, ERP systems, etc.
- Identifying External Data Sources: Third-party data providers, market research, social media, etc.
- Determining Data Types: Structured data, for example, includes databases or spreadsheets, and unstructured data covers emails, social media reviews, and images.
- Outlining Data Acquisition Methods: The available methods are web scraping, API integrations, manual entry, or third-party data partnerships.
- Planning Data Integration: Outlining how data will be combined from multiple sources and how its unified view will be ensured.
Step 5: Laying the Data Architecture Foundation
A solid data architecture can be considered to be the backbone of the strategy, so here are the key components that should be defined during this step.
- Data Storage: Based on business needs, the selection of databases, data lakes, and data warehouses should be made.
- Data Integration: Determining how the data will move between various systems like CRM, ERP, and BI tools and form a unified view of the organization’s data.
- Data Processing: Selecting the right processing engines for real-time and batch data.
Step 6: Deciding on Data Management Approach
There are two distinctive approaches to data management. The first is known as offensive data management and the second is defensive. Offensive data management is all about driving business growth and gaining competitive advantage by using data proactively. It focuses on the ability to act on insights quickly, emphasizing flexibility and agility.
The defensive approach, on the other hand, prioritizes data security, ensuring compliance, and minimizing any possible risks of data breaches, over a rapid sprint for innovation.
Still, in the real world, organizations might as well adopt a hybrid approach to data management, and balance between growth and robust protection. Regardless of the chosen approach, it is necessary to specify data management practices that will guide the entire lifecycle of data. These practices include:
- Data Collection: Methods for collecting relevant data.
- Data Storage: Efficiently storing data in compliance with regulations and cost estimates.
- Data Usage: Ensuring only the right people will have access to the information.
- Data Sharing: Ways of sharing data across departments.
- Data Archiving and Deletion: Setting policies for long-term storage and removing obsolete data for storage cost optimization.
Step 7: Choosing Analytical Approaches and Tools
This stage is for determining analytical methods the organization will use, as well as selecting the most suitable tools for obtaining actionable insights:
- Choosing Analytical Approaches: Deciding between descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, as mentioned previously.
- Selecting Analytics Tools: Determining which of the most effective off-the-shelf solutions will work the best.
- Integrating Insights Into Decision-Making: Work the ways to embed analytics into actual business workflows.
Step 8: Choosing the Right Technology and Tools
Along with data strategy, the organization should decide on a suitable stack of technologies and tools. The main categories include:
- Data Integration Tools: ETL tools like Talend or Apache NiFi.
- Analytics Platforms: Top solutions include Google Cloud, AWS, or Azure.
- Data Visualization: Tools like Power BI, Tableau, or Qlik.
Step 9: Elaborating Data Governance Policies
Data governance ensures that data is used responsibly and meets all necessary quality standards. This involves:
- Establishing Data Governance Policies.
- Defining Roles and Responsibilities.
- Adhering to Industry Standards and Legal Regulations.
- Ensuring Data Quality Management.
Step 10: Tech Talent Acquisition and/or Training
Next, it is necessary to consider the skills that are required to implement the data strategy framework. Depending on its intricacies, it may involve hiring additional specialized staff or providing extensive training programs to train the employees in data analytics, data governance, or data management.
Step 11: Change Management
Like with implementing any other organizational practice, managing change is required. The change management plan can include:
- Creating a clear communication approach with stakeholders.
- Proactively addressing any concerns regarding changes
- Keeping teams informed on all necessary aspects throughout the implementation.
Step 12: Developing a Data Strategy Roadmap
Now, it’s time to create a clear implementation roadmap with specific timelines, milestones, and resource allocation, taking into consideration potential risks. The main areas to cover include:
- Define the key objectives and deliverables for each phase of the project.
- Regularly review and adjust the roadmap as needed to address any unforeseen challenges or changes in business priorities.
We, at SPD Technology, can help you with any aspect of the data strategy roadmap, if you encounter any difficulties at this stage.
Step 13: Continuous Improvement
Any data strategy framework should be built to be adaptable, so the company has to be prepared for ongoing evaluation and always have some room for improvement as the business grows and technologies evolve, ensuring the long-term success of this initiative.
Specific actions the organization might take at this stage include:
- Regularly tracking the performance of the chosen data strategies by measuring KPIs.
- Periodically auditing existing data to identify and address possible inaccuracies, inconsistencies, or missing data.
- Reviewing how the data strategy matches the evolving business goals.
- Establishing structured feedback channels for communication with the users to continuously improve data accessibility, reporting tools, and analytics capabilities.
- Following the evolution of technology and updating your data platforms and tools accordingly.
Data Strategy Framework Development Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Now, that we discussed the process of creating a data strategy framework, let’s talk about some challenges you may encounter along the way.
Lack of Communication
There might be a risk of collecting and analyzing the wrong types of data, which will turn into a big problem when it comes to implementation. Additionally, stakeholders may want to collect all data possible without a clear direction of what to do with it, however, only experts can determine what data is valuable for future processes. Therefore, clear communication between business leaders and data teams is required during the development of the Data Strategy Framework, to prevent these issues.
To overcome this challenge, we suggest implementing a structured communication process right from the start. To ensure everyone is on the same page, we schedule collaborative workshops involving business leaders, project managers, and data experts. Regular feedback sessions are also integrated to ensure alignment.
Data Silos
It is common when data in organizations are scattered across entirely different platforms and departments, and stored in different formats. These data silos result in fragmentation, which can hinder having a unified data strategy. So, before developing a data strategy framework, it is vital to ensure that all data is accessible and well-governed across all departments and that there are no parts of the organization that own their unique pieces of information inaccessible for others.
When encountering this challenge, we start with a comprehensive data audit to identify where critical information across departments is located. We obtain a clear understanding of the silos’ scope and can incorporate a detailed data integration plan into the data strategy framework. Our plan outlines specific steps for centralizing and standardizing data that must be completed before moving forward with implementation.
Take a look at our dedicated article to discover more about the power of data integration and the way it prevents data silos from occurring!
Resistance to Change
The management and employees might resist changes because of uncertainty and potential disruption of established processes. To deal with this, it is necessary to provide clear communication, training, and support for everyone involved, and communicate the benefits of a new strategy for the organization and individuals. Securing stakeholder buy-in and fostering a data-driven culture may require extensive advocacy and educational efforts, but it is necessary to do so before moving to implementation.
To address management resistance to adopting a data-driven decision-making process, we integrate change management strategies directly into the data strategy framework, which includes planning training sessions to familiarize teams with the upcoming changes and developing a clear communication roadmap to keep everyone informed.

Dmytro Tymofiiev
Delivery Director at SPD Technology
“One of the most effective solutions to this is to involve employees in the planning of the new strategy, listening to their input, addressing concerns, and empowering them to become a part of the new framework.”
In one of our projects, we successfully dealt with all data-related challenges while rebuilding the client’s platform according to the current industry standards and achieved a 10x performance boost by replacing legacy technologies with modern ones.
Why Consider Professional Data Strategy Consulting Services?
Developing an effective data strategy framework requires not only deep expertise and experience in a particular industry but also a highly tailored approach with a robust analysis of your organization. Leveraging consulting services from an experienced developer is a good idea due to the cross-industrial experience of a vendor and proficiency in proven methodologies and best practices. You will avoid some common mistakes and save you time and money for more valuable areas of your business. Speaking of time, with the help of the consultants, you will be able to fast-track the development process and move to the implementation phase faster.
Ultimately, with the help of consulting services, you will get a clear framework with cost-effective ways to manage your data infrastructure, while identifying and mitigating any possible risks when you move to the implementation.
Why Partner with SPD for Delivering Data Strategy Framework?
We believe that letting us develop a data strategy framework is a great decision because we typically work with our clients from the initial strategy phase through implementation and ongoing management, offering end-to-end services. With this holistic approach, we understand how to turn your investment in data into tangible business value and eventual revenue, always setting a strong ROI focus as a priority.
Our frameworks are future-proofed since they are scalable by design and prepared for future incorporation of new data sources, compliance with changing security requirements, and integration of modern analytical tools.
Conclusion
A well-crafted data strategy framework can be that one missing element to elevate your business to an entirely new level, making a paradigm shift in your respective market. As reported by Exploding Topics, 91.9% of organizations achieved measurable value from data and analytics investments in 2023, and it is safe to say that in 2024 we should expect even more impressive results.
In addition to unlocking transformative insights, driving innovation, and positioning your organization, having a data and analytics strategy framework can open new opportunities for business lines you don’t initially plan, for example, the integration of custom AI solutions that typically require a lot of accurate data to train upon and deliver value.
For example, within one of our projects, we successfully delivered an AI-powered Social Media Analytics Tool for a Global B2B Data Research & Analysis Company serving 2000+ enterprise clients. Our product automates data collection, processing, and metrics calculation, saving countless hours of human labor.
As a part of our data strategy consulting service, our team of data experts would be glad to help you transform data into the most valuable asset. Together, we will build a foundation for developing a data strategy framework that will enable data-supported decision-making, increase ROI on data initiatives, and provide you with a clear roadmap for data-driven success. Our data analytics experts will deliver customized data strategies that drive tangible business outcomes for your organization, so feel free to schedule a call anytime!
FAQ
What is a data strategy framework?
This is a detailed and structured plan that outlines how an organization will use its data assets to move towards set business goals. This is a blueprint of how data is collected, stored, processed, and analyzed to improve decision-making and maximize competitive advantages. A well-defined data strategy helps organizations reduce compliance risks, improve data quality, make valuable information available to key decision-makers, and allow them to leverage it.


