When it comes to going serverless, the majority of organizations are drawn to its promise of lower costs, faster delivery, and effortless scale, yet every one of these benefits comes with a corresponding trade-off. However, making the wrong choice can lead to misaligned projects and budget overruns, which is why a clear understanding of the serverless computing pros and cons is essential.
This article offers a clear-eyed look at the advantages and disadvantages of serverless architecture and identifies the specific business cases where it creates the most value. That’s why the central question isn’t just whether serverless works, but whether it’s the right fit for your business. Let’s find it out.
What Is Serverless Architecture
Serverless architecture follows a cloud computing model where the provider is responsible for all aspects of infrastructure management: from provisioning to scaling. The goal of a serverless architecture is to eliminate infrastructure overhead, letting your teams concentrate on building features, not maintaining hardware, even though your code still runs on the provider’s servers. These are some of the core serverless architecture benefits.
Think of serverless architecture as outsourcing your server management to the cloud provider. Instead of buying, provisioning, and maintaining servers that sit idle much of the time, you simply deploy your application as a set of functions that run only when needed. This model is event-driven: a user action or data change triggers a function, and you pay only for the compute time it uses, after which it shuts down.
Oleksandr Boiko
Delivery Director at SPD Technology
“Serverless isn’t about having no servers; it’s about having no server problems. It allows leaders to redirect their engineering talent from infrastructure maintenance to building features that win markets.”
The approach truly changes operational thinking and shows why many consider serverless the future of software architecture. Major cloud platforms offer this model of outsourced infrastructure management as the core offering. Each provides a robust ecosystem built around its flagship Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) product, which is the engine that drives serverless computing.
For example, Amazon Web Services broadly defined the category with AWS Lambda. Microsoft offers deeply integrated Azure Functions, and Google provides highly scalable Cloud Run functions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Serverless Architecture
Adopting serverless is more like a strategic business decision with distinct trade-offs than a simple technical switch. Understanding the balance of these serverless architecture pros and cons is the first step toward making an informed choice that aligns with your company’s goals.
Advantages of Serverless Computing
The upsides of serverless often translate directly into competitive advantages.
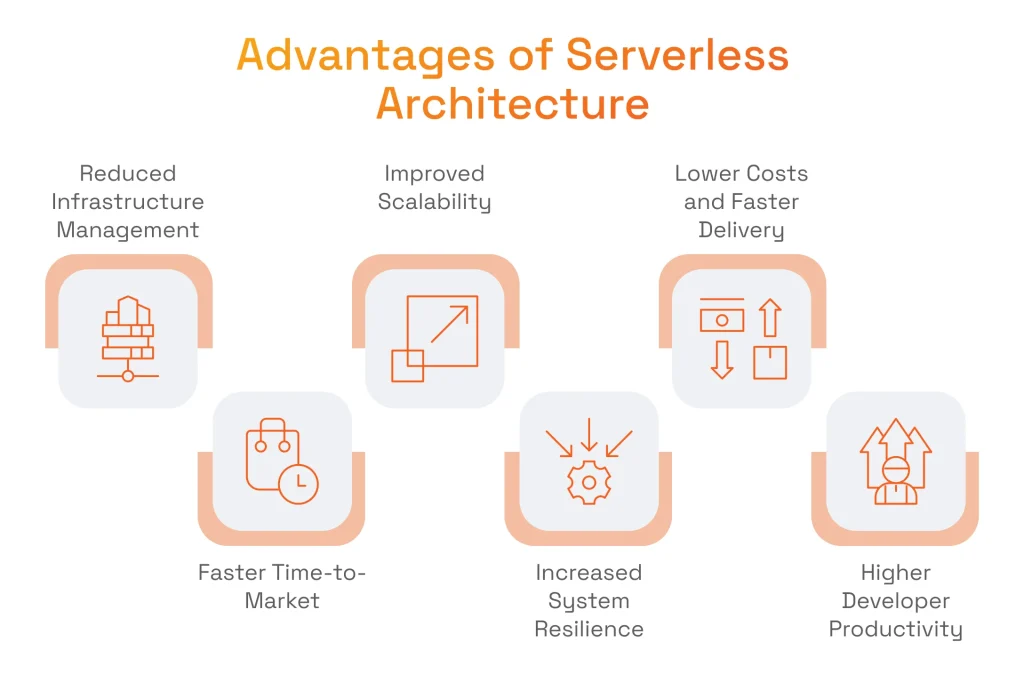
Reduced Infrastructure Management Effort
Serverless abstracts away the day-to-day grind of managing servers. This means your most valuable engineers are no longer bogged down with patching operating systems or planning capacity. Instead of spending their time on infrastructure maintenance, they can focus on building and refining the products that generate revenue. It’s a direct reallocation of talent from operational overhead to innovation, one of the primary advantages of serverless architecture.
Improved Scalability
A serverless application scales automatically in response to demand. If a marketing campaign drives a thousand concurrent users to your site, the architecture handles it. When traffic subsides, it scales back down.
Elasticity means you can confidently seize market opportunities without the fear of your infrastructure failing under pressure. The scalability factor also generates vast amounts of operational and user data, which can be harnessed through effective data analytics services that drive business insights and maximize the benefits of serverless architecture.
Lower Upfront and Idle Costs
With traditional infrastructure, you pay for capacity, whether you use it or not. Serverless shifts your spending to a pay-per-use model, eliminating costs for idle resources. This aligns perfectly with modern FinOps principles, which transform capital expenditures into predictable operational expenses.
For new projects or applications with fluctuating workloads, this model drastically lowers the financial barrier to entry and minimizes waste. This approach requires diligent cloud cost optimization and FinOps to maximize returns, while providing unmatched financial flexibility.
Faster Time-to-Market
Because teams aren’t provisioning servers or configuring environments, the development lifecycle is significantly shorter. Developers can deploy new features or entire applications one function at a time, allowing for rapid iteration and feedback.
Speed is a powerful business driver, which helps you respond to market needs and release products faster than competitors who are still managing their infrastructure. These are significant advantages of serverless architecture for any competitive business.
Increased System Resilience
Cloud providers build their serverless platforms with high availability and fault tolerance in mind. The infrastructure is inherently distributed across multiple availability zones. A failure in one instance doesn’t bring down your entire application; the provider simply routes traffic to a healthy one.
Built-in resilience means less downtime and a more reliable service for your customers, without requiring a dedicated team to architect it.
Higher Developer Productivity
Serverless allows developers to focus on writing business logic. By using pre-built backend services for tasks such as authentication or database management (Backend-as-a-Service), they avoid reinventing the wheel.
The focus on the core application, combined with a simplified deployment process, enables smaller and more focused teams to accomplish more in less time, demonstrating further advantages of serverless computing that lead to a direct increase in engineering efficiency. This efficiency is a core goal of modern serverless architecture development, which also makes serverless an excellent foundation for advanced applications.
For example, deploying machine learning models becomes more manageable when the underlying infrastructure is handled automatically. This is where specialized expertise in areas like MLOps consulting helps streamline the deployment and management of AI workloads efficiently.
Cons of Serverless Computing
The challenges of serverless are not reasons to avoid it, but risks to be managed. Acknowledging them is critical for building a sustainable and effective serverless strategy.
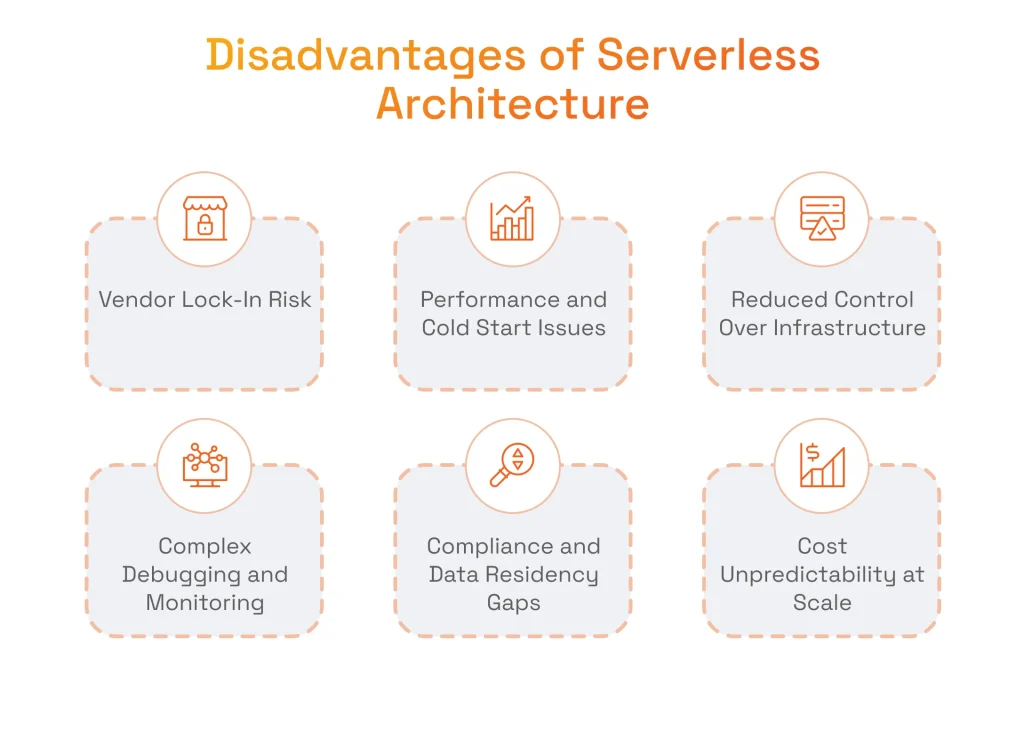
Vendor Lock-In Risk
When you build on a serverless platform, you are integrating deeply with a specific cloud provider’s ecosystem. This dependency can accelerate development, but it also makes migrating to another provider difficult and costly. Each platform has proprietary services and APIs that don’t have direct equivalents elsewhere. To mitigate this risk, you need a strategic approach to architecture that is designed with future flexibility in mind. These are some of the primary cons of serverless computing.
Oleksandr Boiko
Delivery Director at SPD Technology
“The pay-per-use model is a double-edged sword. Without disciplined governance and a deep understanding of your workloads, the promise of cost savings can quickly turn into a story of unpredictable expenses.”
Performance Issues from Cold Starts
How do cold starts impact serverless performance? When a function is inactive, the provider spins it down. The first request after a period of idleness experiences a delay, known as a “cold start,” while a new instance is being initialized. The latency of milliseconds to seconds is negligible for background tasks, but can be detrimental to user-facing applications, where every moment counts. This latency is one of the most debated serverless computing pros and cons, particularly when evaluating the pros and cons of serverless for real-time data.
Reduced Control Over Infrastructure
The abstraction that makes serverless so powerful is also a limitation. You have no control over the underlying hardware, operating system, or runtime environment. If your application requires a specific OS version or specialized hardware configurations, serverless may not be a fit. You are also bound by the provider’s limits on things like function execution time and memory allocation. To answer the question of which of the following is not an advantage of a serverless architecture, this lack of control is a primary candidate.
Complex Debugging and Monitoring
Troubleshooting a problem in a distributed, event-driven system is more complex than in a monolith. A single user request might trigger a chain of functions across multiple services. Pinpointing the root cause of an error requires specialized observability tools and a different mindset. Without them, your team can spend more time diagnosing issues than fixing them, impacting system reliability. Such complexity is a critical point in the debate over the advantages and disadvantages of serverless architecture.
Compliance and Data Residency Challenges
What are the biggest drawbacks or limitations of serverless computing? For many, it’s compliance. In a serverless environment, you don’t always know the exact physical location where your code is running. Ensuring that sensitive data is processed only within specific geographic boundaries requires careful configuration and a deep understanding of your provider’s capabilities. This is especially true given the increasing serverless adoption in Europe and its strict data laws.
Cost Unpredictability at Scale
The pay-per-use model is efficient but can be unpredictable. A bug causing a function to run in an infinite loop or a sudden, massive spike in traffic can lead to a surprisingly large bill. While serverless is often cost-effective, it demands robust monitoring, budget alerts, and cost governance practices to prevent runaway spending. The cost savings are not automatic; they must be managed.
Pros and Cons of Serverless Architecture: Finding the Balance for Your Business
Knowing the trade-offs is one thing; knowing where to apply them is another. Serverless isn’t a universal solution, but for particular business challenges, it offers a distinct strategic advantage. Below are some of the common use cases when a serverless approach makes the most sense.
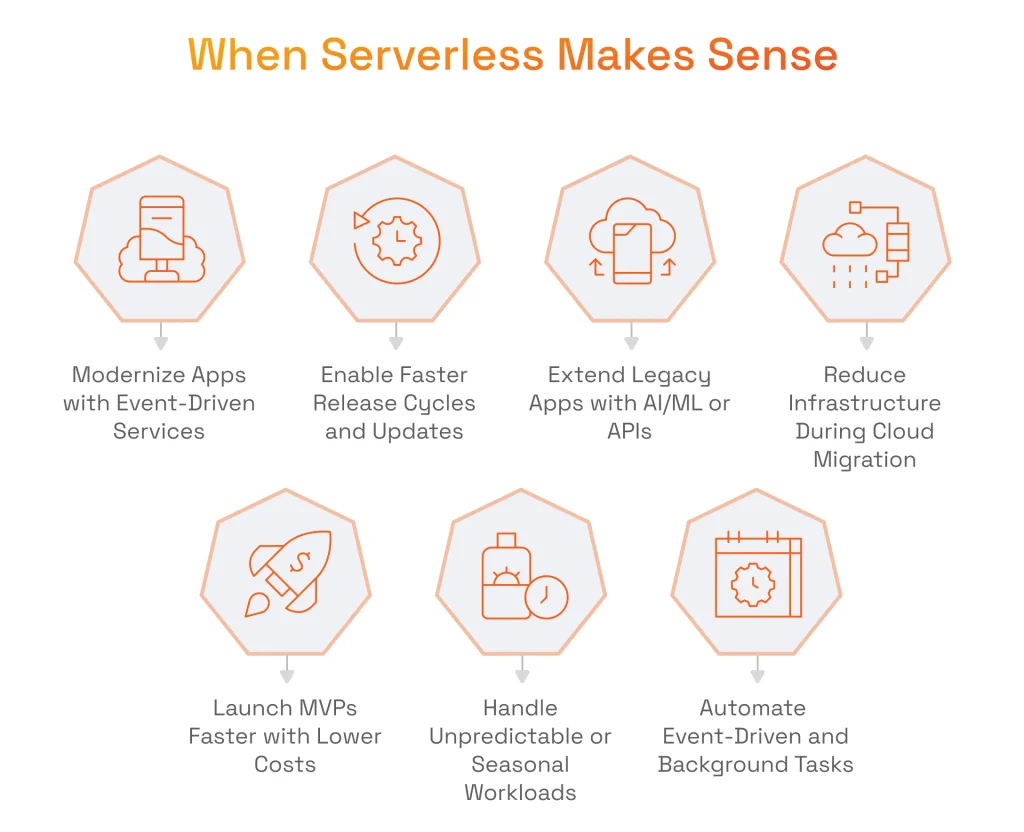
Serverless in Application Modernization Initiatives
Serverless offers a pragmatic path for legacy application modernization, but it is very important to understand the pros and cons of serverless architecture for such projects. Instead of a risky “big bang” rewrite, you can chip away at legacy code, replacing pieces with nimble event-driven microservices.
Are outdated systems holding back your business growth?
Discover the importance of legacy system modernization in our detailed guide.
Serverless during Cloud Migration
Moving workloads to the cloud often means trading one set of management problems for another. Serverless changes that equation. It enables you to re-platform applications into a cloud-native environment and eliminate the burden of server management. Thus, you can immediately reduce operational overhead and maximize serverless architecture benefits.
The serverless approach accelerates the migration process and ensures that your workloads can achieve effective serverless scalability from day one. This strategy can de-risk the entire transition, a core focus of our cloud migration services.
Serverless for MVPs and Rapid Prototyping
The pay-per-use model of serverless makes it the ideal engine for innovation. You can launch a minimum viable product (MVP) and test a business idea with minimal upfront investment in infrastructure. The operational overhead is nearly zero, and the architecture scales instantly if your idea takes off. It’s the leanest way to bring a product to market and validate its potential without being locked into costly long-term infrastructure, which shows the clear benefits of serverless architecture for startups.
Serverless for Applications with Unpredictable Workloads
Many business applications face fluctuating demand. Think of an e-commerce platform during a flash sale or a reporting system at the end of the quarter. Serverless excels in this area.
Your workloads can automatically scale to handle massive, sudden spikes in traffic and then scale back down to zero when the demand subsides. Thus, you avoid paying for idle servers during quiet periods and ensure you only pay for the value you deliver.
Serverless for Event-Driven Use Cases
Serverless is the native architecture for a world of real-time triggers. It’s ideal for IoT solutions that process irregular data streams from thousands of devices, or for automating background tasks such as image processing after a file upload.
Use cases like real-time fraud detection, payment processing, and chatbots are a natural fit, as they require immediate isolated responses to specific events. We’ve seen firsthand how a well-implemented serverless architecture for an asset management analytics app can deliver transformative results in this area.
Why Do You Need a Tech Partner to Tap into the Benefits of Serverless Architecture?
Knowing the pros, cons, and use cases is the first step. The next is execution, and the gap between theory and successful implementation is where many serverless initiatives fail. The right technology partner isn’t just a vendor; they are a strategic guide through a complex transition, helping you reap the advantages of serverless computing. The key is identifying the right fit, knowing why to use serverless architecture, and acknowledging why you need a tech partner for serverless implementation.

- High risk of failure without expertise
Misjudging which workloads are suitable for serverless environments or making poor architectural choices can lead to failed projects and wasted investment. An experienced partner validates the business case first.
- Complexity of designing future-proof systems
A DIY serverless adoption often results in vendor lock-in or architectures that can’t scale with business growth. A partner designs for long-term flexibility, not just short-term wins. This is a core principle of effective serverless architecture development.
- Hidden migration and modernization pitfalls
Moving from a monolith to serverless is filled with risks, such as performance gaps, downtime, and integration failures. Experts have navigated this transition before and know how to mitigate the risks associated with the process, having mastered the serverless pros and cons.
- Uncontrolled costs at scale
Many companies are shocked by their first large serverless bill. Costs can escalate without constant monitoring and optimization, turning a potential saving into a liability.
- Compliance and security gaps
Overlooking data residency rules, industry regulations, or security best practices is not an option. A partner ensures your architecture is compliant and secure from the ground up.
- Lack of operational visibility
Debugging and monitoring distributed systems are notoriously difficult. Without the right observability strategy, your business risks poor reliability and a degraded customer experience.
- Disconnect between tech and business strategy
Adopting serverless technology without clear goals often results in solutions that fail to deliver a measurable return. A strategic partner ensures the technology serves the business, not the other way around.
Understanding the technology strategy consulting benefits is key to bridging this gap and ensuring your architectural choices deliver measurable ROI.
Conclusion
Serverless offers a powerful model for business agility and operational efficiency. It is not a universal fix, but a strategic tool. The risks, from vendor lock-in to performance quirks, are not deal-breakers; they are business variables that can be managed with a deliberate, expert-led strategy.
When you’re ready to translate the pros and cons into a concrete plan, our application modernization experts can help you build a serverless architecture that delivers measurable results. Contact us today to discuss your project.
FAQs
When is serverless not a good choice for my application?
It’s a poor fit for applications with high, predictable traffic, where dedicated resources are cheaper. Long-running processes or workloads needing specific hardware or OS control are also better suited for containers or virtual machines.
What compliance or GDPR concerns exist with serverless in the EU?
GDPR and data residency are critical. You must explicitly configure your cloud provider’s functions to run only within EU regions to ensure compliance. This requires careful setup and validation to prevent data from being processed elsewhere.
Is serverless architecture actually cheaper than containers or VMs?
Not always. It’s cheaper for variable or low-traffic workloads by eliminating idle costs. For applications with high, sustained traffic, the pay-per-use model can become more expensive than reserved containers or VMs.

