The sweeping growth of eCommerce over the past decade boggles the mind: according to Grand View Research, the eCommerce sales are projected to constitute $8.1 billion in 2026.
The pace at which eCommerce has been growing has created the need to improve the business processes within it and look for new ways of meeting the ever more sophisticated demands of the ever growing eCommerce audiences. The advent of marketplaces (like, for example, eBay and Amazon) became the true game changer: the possibility for buyers and sellers to easily switch roles multiple times whenever required necessitated introducing a payment-handling scheme that would not require opening a merchant account every time it was required. And this is how the payment facilitator (or PayFac) came into being.
In 2024, becoming a PayFac could be a worth-considering venture, so before you start, let’s dwell on the essence of payment facilitation as a business and discover its advantages, while keeping technical and compliance considerations in mind.
What Is Payment Facilitation?
Payment facilitation means an approach based on the aggregation of payments by a party called PayFac (also referred to as a merchant service provider) that provides a payment gateway and collects payments from merchants on behalf of an acquirer. Thus, according to the payment facilitation definition, this approach eliminates the hassle of opening traditional accounts for merchants, enabling faster and more seamless transaction processing. PayFacs allow merchants to accept credit cards, debit cards, as well as some other electronic payments.
Good payment facilitation examples are such well-known providers as Stripe, PayPal, Stax Stripe, and many others. In addition, there are also banking institutions that offer merchant services, like, for example, Chase Bank or Wells Fargo.Next, we’ll use our vast experience in fintech and eCommerce software development to look at how PayFac works in more detail.
Traditional Acquiring Vs. Payment Facilitation
To better understand the meaning and benefits behind PayFacs, one should look at the several illustrative differences between facilitation of payments and traditional acquiring.
Traditional acquiring kicks off with a merchant signing a contract with an acquirer, or financial institution that then accepts and processes payments on their behalf, acting as an intermediary between the merchant and a credit card network, such as, for example, Mastercard. With payment facilitation, a merchant doesn’t have to go through the lengthy hassle of opening a merchant account (the procedure may take weeks) and dealing with lots of the related paperwork.
In the case of traditional acquiring, a merchant uses an account with their bank to accept payments of all the types they deal with. With payment facilitation, a merchant uses PayFac’s master bank account: they can receive payments quickly and handle all their transactions centrally, which spares them a great deal of daily drudgery.
Lastly, with payment facilitation, merchants don’t have to work with several financial providers separately.
The Functions Payment Facilitators Perform
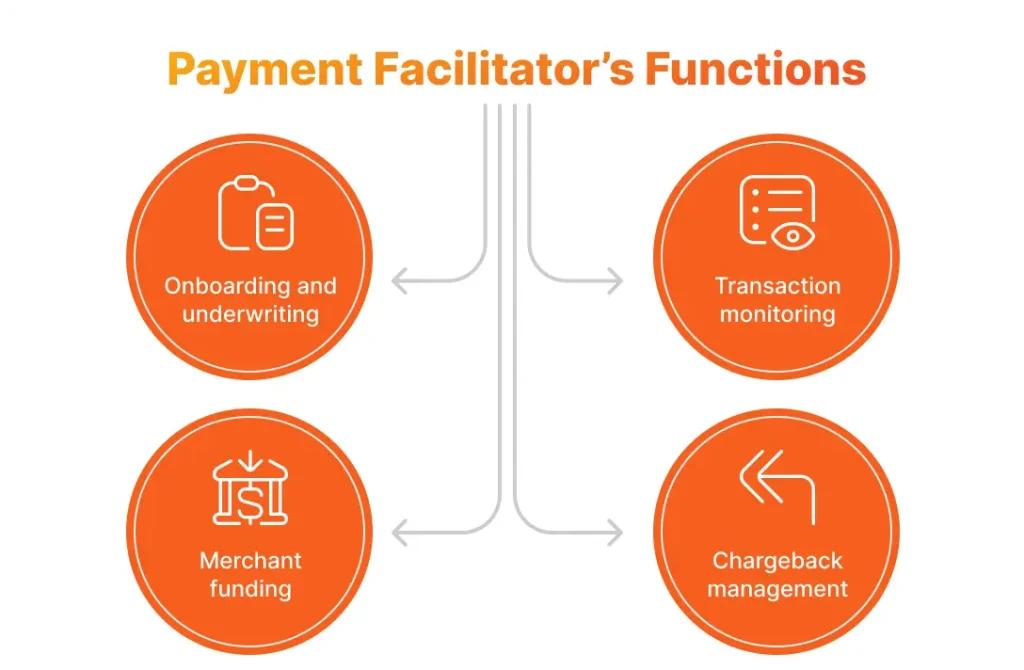
Onboarding and Underwriting
Just like a merchant bank, a PayFac is obliged to properly onboard a merchant. This means that prior to beginning to receive payments via this PayFac, a merchant must undergo a procedure called underwriting, whereby the merchant is vetted with a view to making sure they are not associated with any negative factors (e.g. corruption, bribery, fraud, or other unethical practices).
Underwriting renders the merchant-PayFac relationship compliant with the applicable regulations. In particular, this includes a KYC procedure with checks against various black lists, like, for example, Mastercard’s Master Alert to Control High-Risk Merchants list. In most instances, PayFacs use specialized KYC software to automate their onboarding and underwriting procedures. This is a major time-saving convenience for merchants being onboarded.
Transaction Monitoring
A payment facilitators’ obligations as to their merchant clients being bona fide are not limited to the underwriting procedure that takes place at the start of their cooperation. They must also regularly monitor their clients transactions, making sure their activities stay compliant with various Government regulations, as well those imposed by the credit card networks, like, first of all, PCI DSS.
Merchant Funding
To provide a better and more comprehensive service, many payment facilitators engage in funding or paying out of funds that are due to their merchants. This frequently allows them to reduce the time required for payouts to take place and creates another tangible benefit for their client merchants, in particular, SMEs.
Chargeback Management
Along with their acquirers, payment facilitators must get involved in investigations whenever customers dispute charges. They are also liable for the amount of a transaction in the event they cannot recover this amount from the corresponding merchant. In the case of Traditional Acquiring, the process is handled by the issuing bank that approaches the credit card company involved.
How Do Payment Facilitators Work and Make Money?
Payment facilitators are essentially Fintech businesses that allow merchants to centrally accept payments of different types regardless of the credit card network or payment system the payment originates from. To enable this, they open a master merchant account that can be used to accept payments from multiple merchants.
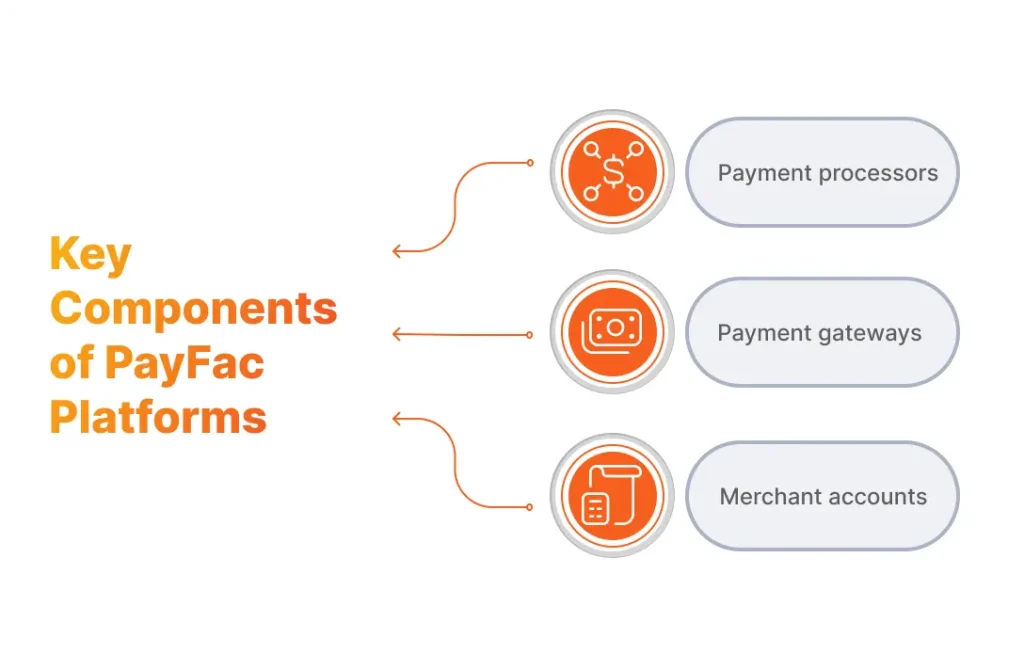
So, how do these components interact to form a PayFac ecosystem?
How Payment Facilitation Works as a Process
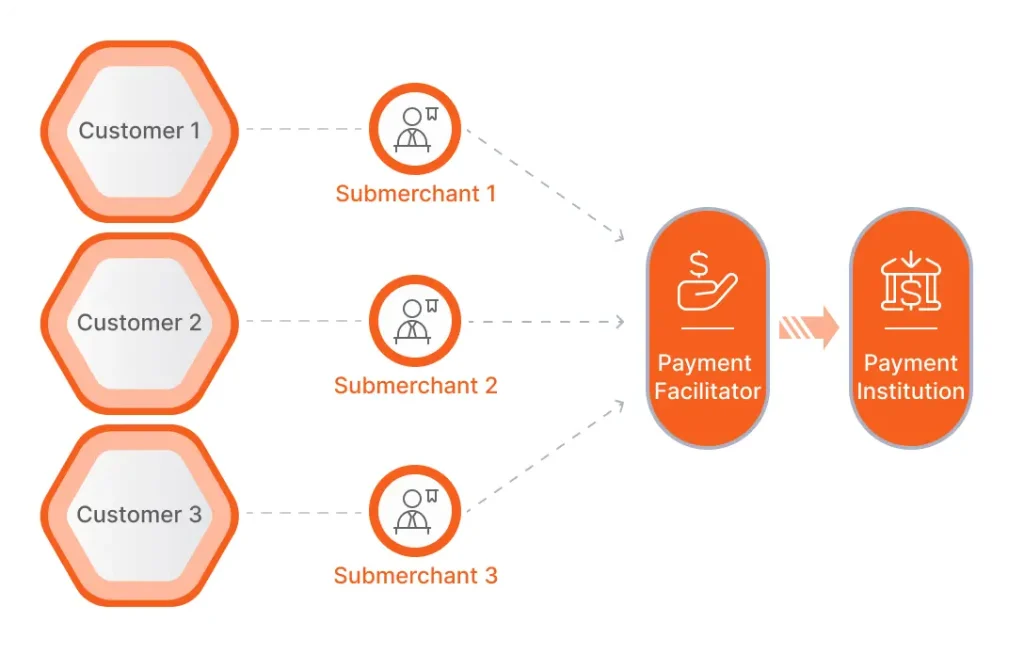
To gain insight into the mechanics of payment facilitation, let’s examine a specific scenario involving a credit card transaction. The processing of this transaction would loom as follows:
- The process starts with a customer making a payment in favor of a sub-merchant using a credit card. The request to authorize the payment is received by the payment processor the PayFac works with.
- The payment processor validates the transaction and forwards it to the corresponding credit card network for further validation. Upon confirmation, the credit card network sends an authorization back to the payment processor.
- Following this, PayFac’s bank settles the transaction and transfers it for further processing.
How Do PayFacs Make Money
According to the payment facilitator model, there are basically two options to profit.
- The first option PayFacs can make money is through the sale of the software that is used to provide their services. PayFacs make use of the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model, and their sub-merchants pay a subscription fee for using this software.
- The second option for PayFacs to profit is to charge a small fee for each of the payments they enable a merchant to make.
Overall, it should be said that payment facilitation as a service can hardly be considered as a high-margin business: PayFacs represent only one of the links in a payment processing ecosystem’s value chain. Because of this, it makes sense to start big in this business niche and allocate more resources from the outset as this will help establish a truly profitable online payment facilitation business.
Advantages of Payment Facilitation
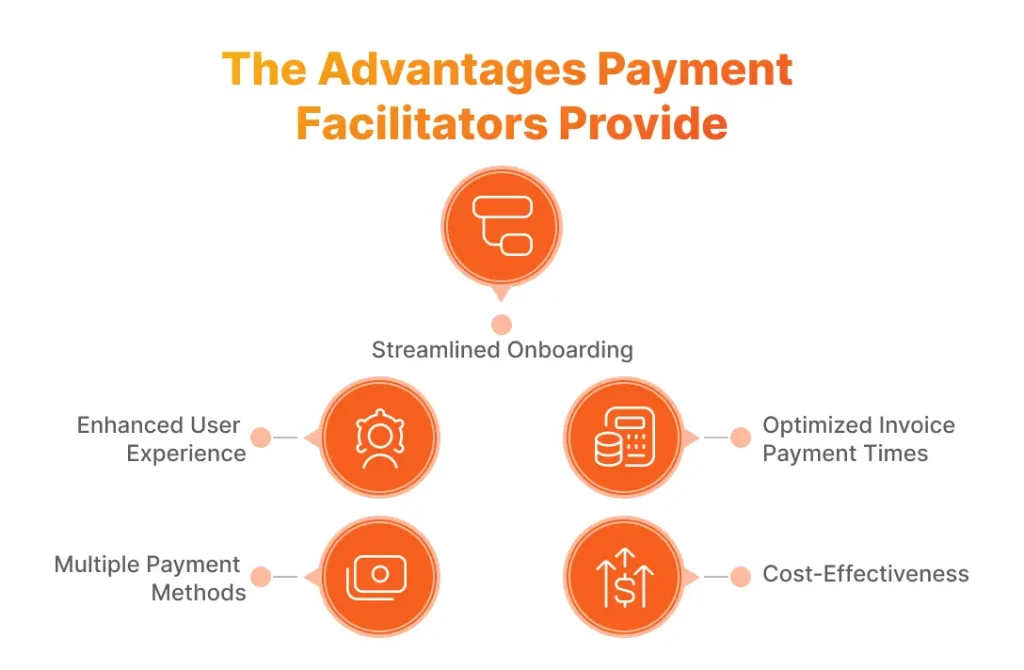
PayFacs bring a diverse host of advantages to the table of the merchants they work with. And these advantages start from the very outset – already with…
Streamlined Onboarding
Traditional payment processing starts with opening merchant accounts with the acquirer’s bank that first needs to be identified by the merchant. Usually, the account opening process is a lengthy procedure that can take weeks and involves a stringent underwriting procedure that is especially difficult for fledgling businesses that lack business history. Payment Facilitation spares merchants the hassle of account opening, dramatically cutting the time spent on the procedure and multiplying their odds to be qualified.
Enhanced User Experience
One can say that PayFacs provide better user experiences for several reasons. Dealing with money, a customer always wants to be safeguarded against error, and the customer experiences PayFacs provide tend to be maximally error-proof. Some 80% of payment facilitators provide 24/7 support, which helps quickly solve the relatively small number of payment-processing issues that arise.
Using a PayFac’s services rids a merchant of the need to regularly transfer funds from their merchant account to their bank account – the PayFac will transfer the money that is due to them from the master merchant account to the company’s bank account, thus regularly saving the merchant both time and effort.
Lastly, it’s relatively easy for payment facilitators to team up with independent software vendors that build software solutions for those businesses that can benefit from the ability to quickly accept payments. This kind of business synergy has come to be known as embedded payments and creates improved customer experiences for small businesses like hairdressers, barber shops, veterinary clinics, and others.
Multiple Payment Methods and Optimized Invoice Payment Times
Working with a payment facilitator allows merchants to quickly encompass a diverse array of payment methods and establish a business presence on online marketplaces. Furthermore, in case of need, they can easily and conveniently impose recurrent payments and expect minimum invoice payment times as it is easy to pay invoices via a payment facilitator.
Cost-Effectiveness
With PayFacs, you pay per-transaction fees while the other payment-processing providers charge monthly fees that they can sometimes combine with per-transaction fees. Additionally, facilitation payment reduces the number of chargebacks, and, as a consequence, the related cost.
Finally, one should also mention that the vast majority of PayFacs also provide their merchants with fraud checks and payment analytics in relation to their customers and payment channels, which makes cooperation with them all the more appealing for their merchant clients.
Payment Facilitation Compliance and Legal Matters
We’ve explained why it’s worth becoming a PayFac, and have found out the strong points a facilitator potentially has to attract a client audience. Let’s now see how to start the process of becoming a PayFac – legal-wise and with regards to several other aspects.
Licensing and Registration
The process of becoming a PayFac kicks off with the candidate business looking for an authorized acquiring bank on whose behalf they will perform payment facilitation. Getting registered with an acquiring bank includes getting registered with the credit card networks. Please note that registering with the credit card networks involves paying a fee. For example, Mastercard and Visa charge $5K annually.
The candidate companies must apply to an acquiring bank, present their complete business plans and financial information, and undergo what is normally a time-consuming and effort-intensive underwriting and approval process. The bank would normally check your business processes and the technology you use with a view to assess your ability to properly underwrite merchants, prevent fraud, and handle chargebacks. Generally, businesses that already have established customer-vetting processes in place pass the procedure more easily. A payment facilitation agreement with an acquiring bank allows the PayFac-to-be to get sponsored for providing facilitation payment services.
In addition to the registration with an acquirer, it is also necessary to purchase the required licenses. The specific licenses to be obtained depend on the countries where your business is based. For example, for the UK this would be the Electronic Money Institution license.
PCI DSS, AML and KYC
As any other entity operating in the financial technology industry, a payment facilitator should be fully compliant with payment processing regulatory requirements, including but not limited to the ones of PCI DSS, PCD2, SOC2, AML and KYC. So, before you get started with establishing a payment facilitation company, make sure to research and understand the regulatory landscape in the region where you operate. For example, PCD2 is a payment data security standard applicable to businesses operating in the EU. PCI DSS, in turn, doesn’t have geographical boundaries and is a global fintech data security standard, pillared upon six main principles while each of which has its specific recommendations and requirements to meet.
Need to make sure your business is sufficiently PCI DSS-compliant?
Our PCI DSS Compliance checklist can be helpful in achieving this goal.
Implementing KYC standards and the other aspects of a full-value AML program is another major aspect of becoming a duly established PayFac. Thus, a PayFac must develop a reliable mechanism of performing the KYC procedure, as well those for risk assessment, transaction monitoring, and staff training.
Fraud Detection and Protection
To become a full-fledged PayFac, your business must implement reliable anti-fraud protection. In order to do this, PayFacs often employ advanced Machine Learning technology.
More particularly, a PayFac must have robust anti-fraud protection in place during the underwriting process with a view to detecting fraudulent merchant applications. This can include checks against various databases and black lists, geolocation checks, and 3d-party validation. Besides, it is also essential to develop functionality that allows detecting fraudulent transactions and preventing the resulting fraudulent chargebacks.
Key Considerations Before Becoming a PayFac
Being a rather low-margin business, online payment facilitation can become a rewarding business only when a PayFac meets several important criteria.
Because of this, one should carefully consider their ability to satisfy these criteria prior to making a decision to kick off.
- Expected ROI. Assessing the odds of your payment facilitation business achieving a positive and sufficient ROI is the primary criterion you should focus on. Carefully calculate all your expenditures and take into account that a PayFac is likely to become profitable only when it starts processing several dozen million transactions.
- Costs. Businesses that want to engage in providing facilitation payment as a service must necessarily be aware of the significant costs they must be prepared to incur. The upfront costs may constitute approximately $500 000 – $2 million, while the recurring annual costs are likely to be several hundred thousand dollars too.
- Payment Infrastructure Development. When becoming a PayFac, you must be ready to invest in an array of high-quality systems to provide the key business processes no PayFac can do without.
In particular, one should be ready to bankroll the development of payment facilitation software, including advanced fraud detection software, and, in some instances, custom payment gateway development. If the latter is not the case and you decide to use an existing payment gateway, one will need to perform a secure and reliable integration with this payment gateway.
Conclusion
Online payment facilitation both creates a number of tangible advantages for merchants in an extensive range of business niches and makes it easy to partner up with software vendors that cater to these merchants. Owing to this, facilitation of payments can become a budding realm of activity for a technology company or startup that wants to profit from the payment industry’s massive growth.
Simultaneously, it is critical to realize that payment facilitation typically requires a significant investment in terms of licenses and payment software development and can become a profitable and future-proof business only when done on a large enough scale. Should you have any question with regard to becoming a PayFac or coping with the related Fintech development challenges, please do feel contact us.
FAQ
What is a payment facilitator?
A payment facilitator or PayFac is a technology business that accepts payments on behalf of an acquiring bank, while offering merchants a host of clear-cut advantages, like much faster onboarding, multiple payment methods, and cost-effectiveness.
How to monetize payment facilitation?
Basically, there are two ways to monetize payment facilitation – charge payment fees and sell payment facilitation software using the SaaS model. Some payment facilitation businesses opt for a licensing business model as well.
What is the difference between payment facilitator vs payment processor?
A payment facilitator provides payments-related services to merchants, while a payment processor acts as an intermediary between banks, merchants, and credit card networks, collecting payment information and sending it to banks and credit card networks.
How to become a payment facilitator?
To become a payment facilitator, a business needs to contract with an acquiring bank, purchase a license, ensure PCI DSS Level 1 compliance, and develop the required software.
